Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
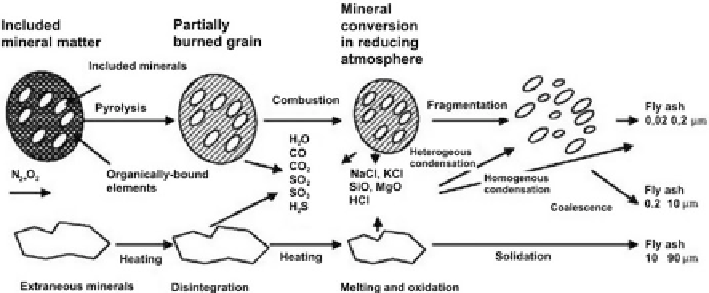
Fig. 4.1 Mechanism of fine ash particle formation in fluidised bed coal-fired thermal power plants
[
1
]
C
n
H
2
nþ
2
þ
ð
n
þ
1
Þ=
2O
2
!
n
C
þ
ð
n
þ
1
Þ
H
2
O
ð
4
:
1
Þ
C
n
H
2
n
þ
n
=
2O
2
!
n
C
þ
n
H
2
O
ð
4
:
2
Þ
C
n
H
n
þ
n
=
4O
2
!
n
C
þ
n
=
2H
2
O
ð
4
:
3
Þ
C
n
H
2
nþ
2
þ
ð
n
þ
5
=
2
Þ
O
2
!
ð
n
3
Þ
C
þ
2CO
þ
CO
2
þ
ð
n
þ
1
Þ
H
2
O
ð
4
:
4
Þ
For any other organic compound used as fuel oil or fuel, the incomplete carbon
oxidation reaction is identical, the functional groups on the main, aliphatic or
aromatic chain generating various oxidation compounds of the C, CO or CO
2
type or organic intermediates with oxygen [
2
]. Several characteristics of particulate
matter produced through incomplete combustion are given in Table
4.1
.
4.2
Inorganic Acids and Bases
Atmospheric oxidation is mediated by free radicals. Unlike oxidation in flame
regime, the energy source for atmospheric oxidation is solar radiation. In lower
atmospheric layers, the photolysis of ozone molecules produces peroxy or hydroxyl
radicals in the presence of water vapour [
2
,
3
]:
O
3
þ
h
υ
!
O
þ
O
2
ð
4
:
5
Þ
O
þ
H
2
O
!
H
2
O
2
ð
4
:
6
Þ
2HO
O
þ
H
2
O
!
ð
4
:
7
Þ
2O
!
O
2
ð
4
:
8
Þ
Ozone molecules, like atomic oxygen and hydroxyl ions, have high reactivity to
any reductive atmospheric compound.