Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
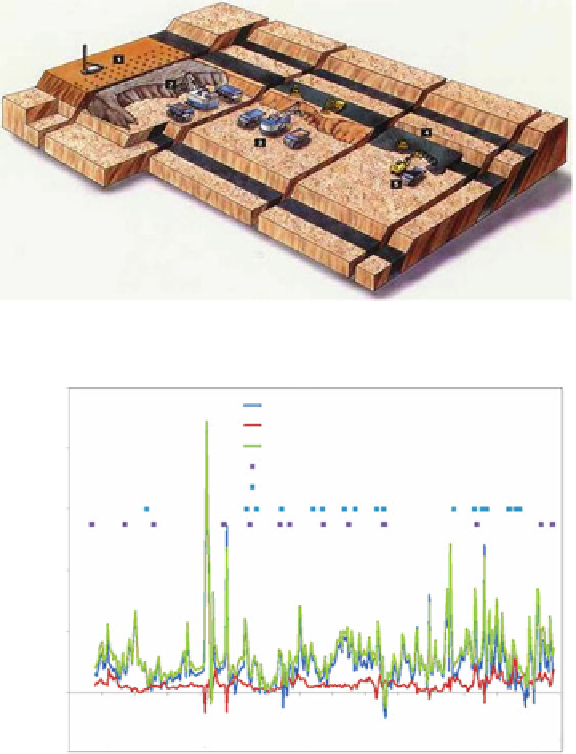
Fig. 3.2 Open-pit coal mining at Greenhills schematic [
16
]
100
PM2.5
PMCoarse
80
PM10
Blasting Events: Ewing Fork #2 Surface Mine
Blasting Events: Horse Creek Surface Mine
60
40
20
0
-20
Date
Fig. 3.3 PM
10
and PM
2.5
variation near coal quarries in the Appalachians (West Virginia) [
20
]
Air pollutants are usually the same when coal is extracted through underground
mining: PM and gas, including also methane (CH
4
), sulphur dioxide (SO
2
), nitrogen
oxides (NO
x
), hydrogen sulphide and carbon monoxide (CO) [
21
].
The mixture of these constituents is called
firedamp
and its presence in mine
galleries can cause explosions and death by intoxication [
22
].
Accurate nanoparticle measurements expressed as PM
2.5
were taken under a
thorough study conducted for several years in several mines of the Appalachian
region. The research results are given in Fig.
3.4
[
11
].
The above results show that the most important fraction of fine particles
expressed as PM
2.5
is not evacuated through airshafts; it originates in open-air