Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
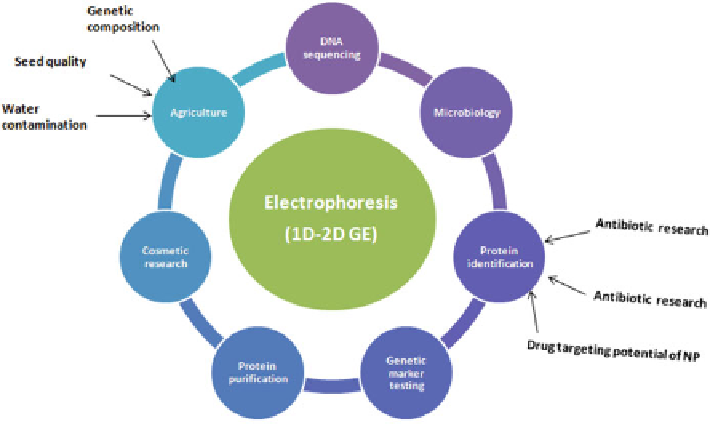
Fig. 15.5 Applications of (1D-2D) electrophoresis gel techniques
abundance, thus providing early justification for downstream analytical steps. A
few applications of profiling include:
A critical modulator of biological activity in the proteome is posttranslational
modifications, or PTMs. 2-D electrophoresis can be used effectively to study PTMs.
2-DE separates charge and size isomers of polypeptides. Hundreds to thousands of
polypeptides can be resolved in a single 2-D PAGE gel and can be quantified,
probed with antibodies (via blotting), tested for posttranslational modifications
(using antibodies/chemical stains specific for each PTM) or extracted for mass
spectrometric analysis. After enrichment of various PTMs of interest, they can be
profiled via 2-DE. Some applications are as follows (Fig.
15.5
):
• Phospho protein expression profiling is used in signal pathway studies. Phos-
phorylated protein pIs shift to a more acidic region on the gel.
• Acetylated protein expression profiling—Acetylation of proteins at their amino
termini or on lysine side chains causes them to shift to a more acidic region on
the gel. Acetylation of proteins can affect protein function, interactions and
subsequent or additional posttranslational modifications.
• Methylated protein expression profiling—Methylation of lysine or arginine
residues shifts their isoelectric points significantly towards the acidic spectrum.
Analysis of protein methylation is particularly important in epigenetic studies.
• Glycosylated protein expression profiling—Glycosylation is both a
cotranslational and posttranslational modification. Attachment of relatively sim-
ple glycans (O-glycosylation) or more complex glycans (N-glycosylation) can
have varying effects on protein molecular weight, pI and protein functions.