Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
repulsion term, ε is the dielectric constant of the medium, and Δ
solv
is the
partial disolvation produced by the partial transfer of electron from the
atomic orbital Ψ
m
to Ψ
n
, or simply the solvation energy.
Klopman further pointed out that various types of interaction can well
recognize in terms of the frontier orbitals,
E
m
*
and
E
n
*
.
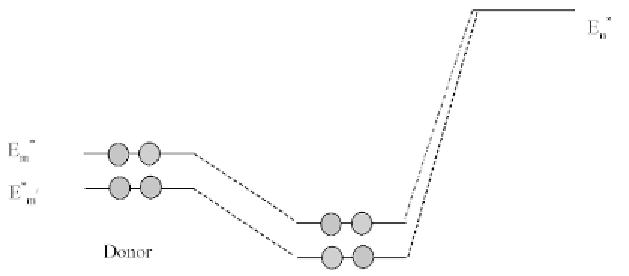
1.2.8.1 CHARGE-CONTROLLED REACTION
When the difference between the frontier orbitals is much larger than 4β
2
,
very little charge transfer occurs and small energy differences between the
various molecular orbitals of each molecule can be neglected, and the total
perturbation energy is primarily determined by the total charges on the two
reagents. Klopman called the reaction as a “charge-controlled reaction.”
Such an effect reflects an ionic-type interaction. It is predominant between
highly charged species, when
E
m
* is very low, that is, when the donor is
difficult to ionize or polarize, and when
E
n
* is very high, that is, when the
acceptor has a low tendency to accept electrons and when both reactants
are strongly solvated, that is, are of small size. It is also enhanced by (i)
small values of β which corresponds to the low tendency to form covalent
bonds, (ii) high Γ value, (iii) small radius, and (iv) low polarizability of the
two reactants (Figure1.1).
FIGURE 1.1
Charge-control effect.
1.2.8.2 FRONTIER-CONTROLLED REACTION
On the other hand, when the two frontier orbitals are nearly degenerate,
that is, │
E
m
*
−
E
n
*│
= 0, then, their interaction becomes predominant, and















Search WWH ::

Custom Search