Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
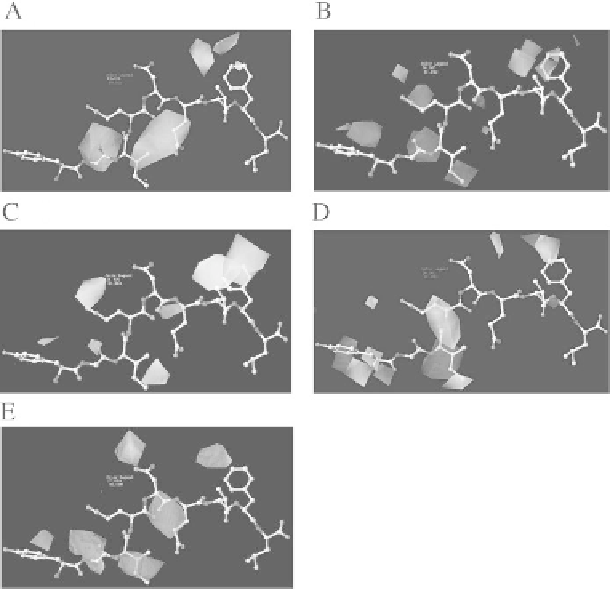
Fig. 4.
H2-D
b
allele: Steric bulk maps (A), electrostatic potentials maps
(B), hydrophobic
interaction maps
(C), H-bond donor maps
(D), H-bond acceptor maps
(E). (A color version
of this figure appears between pages 76 and 77.)
4.4.1 Additive Method - Class I Alleles
The 2D-QSAR additive method has been applied to the peptide binding specificities
of the A3 superfamily human class I alleles: A*1101, A*0301, A*3101, and
A*6801. Sequence analysis showed that only 11 of the residues inside the binding
pockets are polymorphic. A good, if incomplete, consensus was found in the prefer-
ences at the primary anchor positions 2 and 9. Thr and short hydrophobic residues
such as Ala and Ile were favored at P2 and nearly all the peptides bound to A3 alleles
had positively charged residues Arg or Lys at the C-terminus. The amino acids in-
volved in peptide binding are similar in HLA-A2 and the A3 family. Pocket B inter-
acts with the side chain of the residue at position 2, which was one of the anchor
positions in nearly all the MHC class I alleles. Most of the amino acids in pocket B
are conserved in the A2 and A3 families; both families accept hydrophobic residues.
The amino acid at sequence position 9 of the MHC protein is important in peptide
binding in the two families. Alleles (A*3101, A*0301, and A*0201) with small to
medium-sized residues (Phe9 or Thr9) were able to accept residues with long side
chains such as Leu. On the other hand, only small residues such as Ala and Val could
bind to A*6801, A*1101, and A*0206, all of which had the larger residue Tyr9. The