Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
low-throughput and knockout mouse methods may confer lethality, ENU mutagene-
sis results in partial loss of function at much higher levels of throughput.
10.3.2 ENU-Based Phenotype-Driven Mouse Mutagenesis
The primary objective of the ENU mouse mutagenesis project is to identify and
construct mutant lines on a scale such that the whole mutant archive encompasses at
least one mutant for any gene. Worldwide, more than ten large-scale ENU mouse
mutagenesis projects with a genomewide coverage have been initiated.
10.3.2.1 Phase I: Dominant Screens
The identification of useful mutants depends on how meticulously the phenotype
assessment is conducted. All the G1 progenies depicted in Fig. 5 are subject to vari-
ous phenotype screens. The full description of the RIKEN screening platform is
available at the URL http://www.gsc.riken.jp/Mouse/. RIKEN started full screening
in 2000. So far more than 20,000 (Masuya, Nakai, Motegi, Niinaya, Kida, Kaneko,
Aritake, Suzuki, Ishii, Koorikawa, Suzuki, Inoue, Kobayashi, Toki, Wada, Kaneda,
Ishijima, Takahashi, Minowa, Noda, Wakana, Gondo, and Shiroishi 2004) G1 mice
have been screened. The basic screens are modified SHIRPA (
S
mithKline Beecham
Pharmaceuticals,
H
arwell MRC Mouse Genome Centre and Mammalian Genetics
Unit,
I
mperial College School of Medicine at St Mary's,
Ro
yal London Hospital, St
Bartholomew's and the Royal London School of Medicine,
Ph
enotype
A
ssessment)
(Rogers, Fisher, Brown, Peters, Hunter, and Martin 1997) which includes morpho-
logical and behavioral screens. Other additional phenotype screenings include
hematology, urine and serum biochemical analyses.
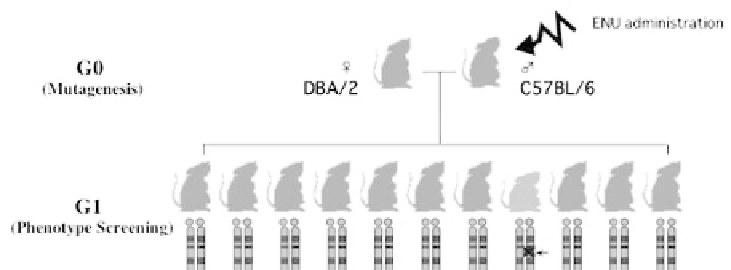
Fig. 5.
Overall scheme of the dominant mutant screening at RIKEN. ENU is administered to
male C57BL/6 inbred mice (abbreviated G0). The ENU-treated males are mated to another
inbred strain DBA/2. All the F1 hybrid offspring, designated as G1, are subjected to exhaus-
tive phenotype screens. In this scheme dominant mutations are collectively identified in a
genomewide manner.