Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
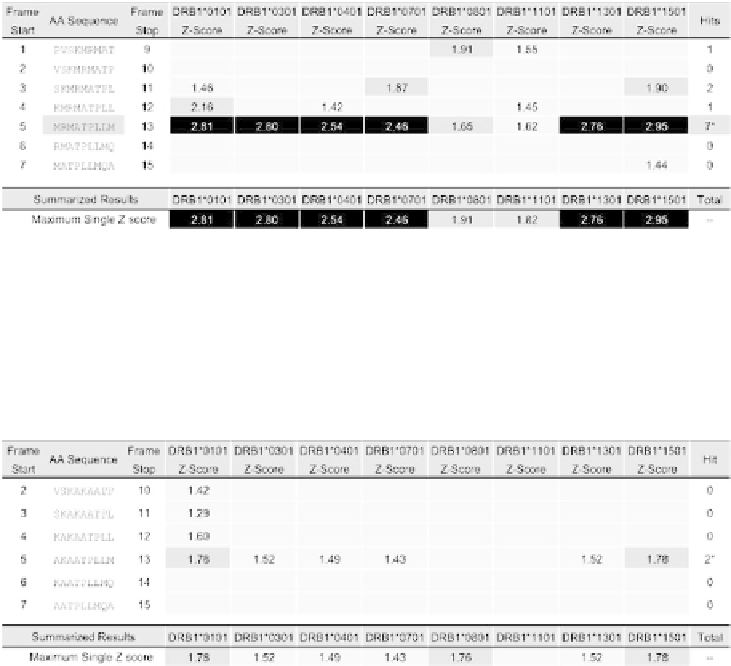
Table 4a.
Z score indicates the potential of a 9-mer frame to bind to a given HLA allele; the
strength of the score is indicated by the shading: top 10%
■
;top 5%
■
;
top 1%
■
. All scores in
the top 5% are considered “hits.” *Frame 107-115 (sequence highlighted) contains four or
more alleles scoring above 1.64 and as such is referred to as an EpiBar. EpiBars have an in-
creased likelihood of binding to multiple HLAs.
Table 4b.
Z score indicates the potential of a 9-mer frame to bind to a given HLA allele; the
strength of the score is indicated by the shading: top 10%
■
;top 5%
■
;
top 1%
■
. All scores in
the top 5% are considered “hits.” Scores below the top 10% are omitted for simplicity. *Frame
5 (sequence highlighted) contains high scores for 2 of the 8 alleles tested as compared to 7 of
the 8 alleles in the parent sequence. The modified CLIP contains no EpiBars. EpiBars (frames
with high scores across at least 4 alleles) have an increased likelihood of binding to multiple
HLAs.
6.4.3 Confirming the Potential of Epitope Clusters
in Vitro
MHC binding assays can be used as the first screen for immunogenicity
in vitro
(Elvin, Potter, Elliott, Cerundolo, and Townsend 1993). These assays confirm the
binding affinity of predicted epitopes for various MHC alleles and are based on
competition between the test peptide and a known binder to recombinant soluble
MHC molecules (Tompkins, Rota, Moore, and Jensen 1993). Since MHC binding
is the first event involved in the stimulation of a T-cell response and is one of the
more critical criteria determining potential immunogenicity, a peptide's ability to
bind to a given MHC can indicate its potential to generate a T-cell response. These
binding assays can also be used to determine whether suggested modifications
would disrupt the binding and presentation of predicted epitope to T cells. How-
ever, processing of the protein antigen is not measured by the binding assay. Thus,