Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
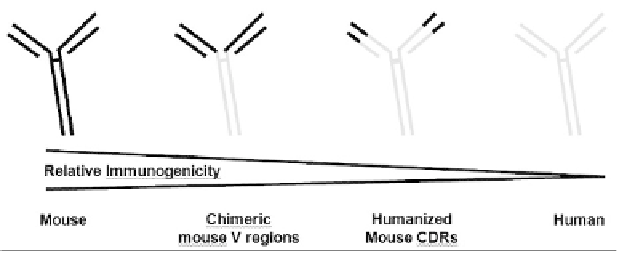
Fig. 1.
Minimal effect of “humanization” on immunogenicity of mAbs. Administration of
murine antibodies such as Campath 1G is associated with the development of antidrug anti-
bodies in as many as 78% of immunocompetent subjects. Minimalization of the murine com-
ponent of the antibody by substituting human constant domains (chimeric and humanized
antibodies) may result in significant reductions in immunogenicity. However, administration
of chimeric antibodies such as Remicade and humanized antibodies such as Campath IH to
immunocompetent subjects has been associated with induction of antibodies in as many as
70% and 63% of subjects, respectively. Administration of fully human antibodies can also
induce immune responses. For example, Humira has been associated with induction of anti-
drug antibodies in 18% of subjects in some studies.
6.2.3.1 Ti B-Cell Activation
Activation of naïve B cells to produce specific antibodies (Abs) via the Ti mecha-
nism involves immune responses to polymeric antigens (Ags) with repeating subunit
structures (e.g., polysaccharides) that are generally not relevant to the use of soluble,
mono-disperse therapeutic proteins; hence, this chapter will not consider them fur-
ther. The Td mechanism is of greater concern as it generates immunological memory,
and also promotes affinity maturation of the Abs and immunoglobulin (Ig) class
switching. In fact, the presence of IgG class antibodies implies that a therapeutic
protein is a
T-cell-dependent (Td) antigen
,
, i.e., isotype switching has occurred.
6.2.3.2 Td B-Cell Activation
In order to induce naïve B cells to react to a Td protein antigen and initiate an adap-
tive immune response, several events must be coordinated, usually within specialized
regions of secondary lymphoid organs (e.g., lymph nodes, spleen). An interaction
between clonally expressed B-cell transmembrane antigen receptor molecules (IgM
Table 2.
T-independent (Ti) and T-dependent (Td) immune response.
T independent
T dependent
No isotype switching
Isotype switching
Low affinity
High affinity
No or low memory
T and B memory