Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
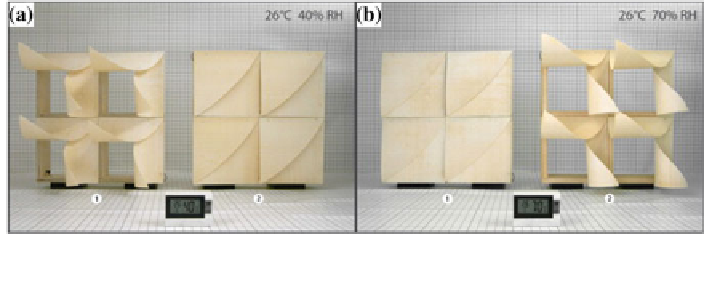
Fig. 5.2 Example of opening and closing behaviour of the Meteorosensitive Architecture
prototypes. (Source Reichert et al. (
2014
), reprinted with permission)
conditions. Figure
5.2
, for instance, shows two configurations, where (a) the
façade closes and (b) opens with increasing relative humidity levels. Many types
of architectural expressions can be achieved by adapting the existing design
concept.
5.3.1.3 Form: Facade
Natural ventilation is a prominent design strategy for low-energy building oper-
ation. Controlling the opening and closing schedules of windows is, however, a
challenging task because the resulting air flow can easily be too high or too low.
''Living glass'' tries to offer a solution to this problem by controlling the opening
of a façade with gill-like slits, looking similar to the mechanism for gaseous
exchange found in aquatic organisms (Geiger
2010
; Linn
2014
). Using strips of
shape memory alloy that expand or contract in response to (man-made) CO
2
concentrations, a perfect balance between façade opening, pressure difference and
momentary ventilation requirements can be achieved.
5.3.1.4 Form: Whole Building
Unmistakably inspired by the wings of a bird, the Burke Brise Soleil, covering the
Quadracci Pavillion at the Milwaukee Art Museum in Wisconsin, is an iconic
piece of architecture (Fig.
5.3
). The eye-catcher consists of 72 steel fins that span
the roof of a 27-m tall glass dome, and collectively open and close with the
opening hours of the museum (Trame
2001
). The morphological resemblance with
a bird is not just cosmetic but also serves a functional purpose. The brise soleil
dynamically protects the sunspace from excessive radiation, but in a form that is
detached from the ornithological background where the façade system took its
inspiration. Moreover, one can argue if this type of shading strategy is actually
effective when compared to more conventional solutions.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search