Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
the system. The effectiveness of this approach will depend on the amount of client buffers as
well as the time required in performing the retransmission. Second, the client could reduce the
effect of data loss by error concealment. The effectiveness will depend on the coding algorithm
employed as well as the type of data lost. In practice, round overflow will be relatively rare as
not only is the overflow probability small, a service operator also rarely runs the media server
at 100% utilization.
4.6 Performance Evaluation
To compare the performance of soft scheduling and hard scheduling, we conducted extensive
simulations using detailed disk models obtained from the DiskSim simulator project [14,
15]. We simulated five modern disk drives from three manufacturers (Quantum Atlas-III,
QuantumAtlas-10K, Seagate Barracuda, Seagate Cheetah, IBM9ES). The diskmodels include
parameters such as seek time, rotational latency, number of disk zones, number of cylinders
per zone, number of sectors per track in each zone, etc. Block sizes of 64KB, 128KB, 256KB,
and 512KB are simulated for each of the five disk models.
4.6.1 Service Round Length Distribution
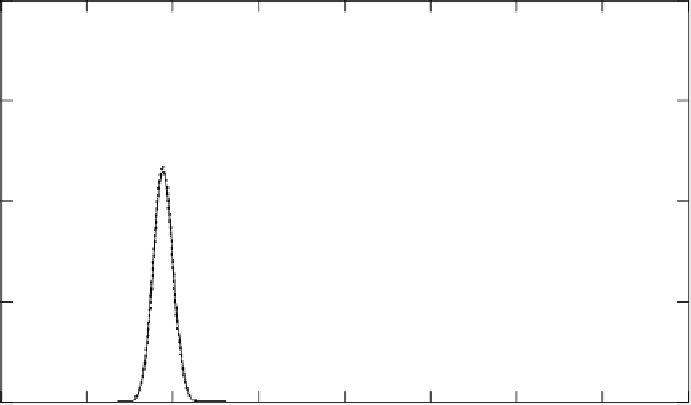
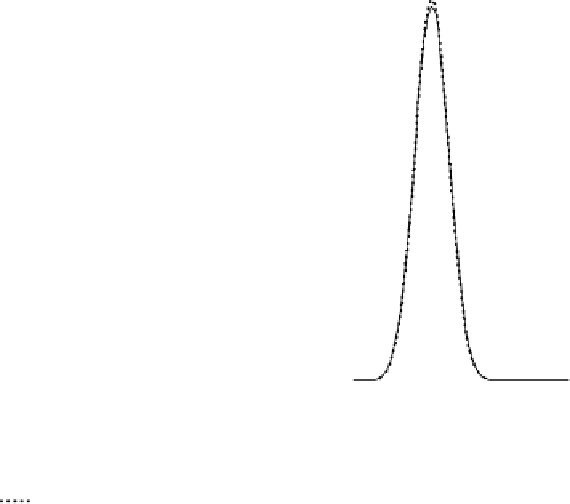
Figure 4.4 shows the round length distribution for the Quantum Atlas-10K disk model
for round sizes of
K
=
10, 20, and 30 respectively. A remarkable observation is that the
0.08
K=30
K=20
0.06
K=10
0.04
0.02
0
0
0.05
0.1
0.15 0.2
0.25
0.3
0.35
0.4
Service Round Length (seconds)
K=10 (Simulated)
K=10 (Normal Approx.)
K=20 (Simulated)
K=20 (Normal Approx.)
K=30 (Simulated)
K=30 (Normal Approx.)
Figure 4.4
Service round length distributions and the corresponding normal approximations








































Search WWH ::

Custom Search