Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
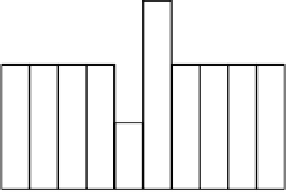
Allocated network bandwidth
. . .
Media bit-rate
Playback Time
(a)
Allocated network bandwidth
. . .
Media bit-rate
Playback Time
Media data transmitted ahead of playback time will need to be
buffered
at the client.
(b)
Figure 1.18
Reducing the peak bit-rate by sending media data ahead of their playback schedule
(a solution with trade-off in client buffer space)
in Figure 1.18 with an admittedly contrived bit-rate pattern where the fifth media segment is
of lower than average bit-rate and the sixth media segment is of higher than average bit-rate.
Applying the work-ahead principle we simply start sending the sixth media segment im-
mediately after sending the fifth media segment. As there is more network bandwidth than is
needed to send the fifth segment, this work-ahead transmission can be done without affecting
the arrival time of the fifth segment. On the other hand, as the sixth media segment is now
transmitted earlier, there is more time for the transmission and so the average transmission rate
can be reduced as well. This can lower the peak bit-rate if the sixth media segment happens to
be the one with the highest bit-rate. Note that for sake of illustration, the example given here is
necessarily simplistic. In general, the media bit-rate profile can vary substantially in both short
and long time scales. However, by combining the principles of trading off time and space, the















Search WWH ::

Custom Search