Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Zone 1
Zone 2
Zone 3
Zone 4
Zone 5
Zone 6
Zone 7
Zone 8
Zone 9
Zone 4 and 9 from a zone pair in WSGP to
accommodate data for static channels
Zone 5 and 8 from a zone pair in WSGP to
accommodate data for static channels
Zone 6 and 7 from a zone pair in WSGP to
accommodate data for static channels
Figure 20.4
Data layout for a disk with
Z
=
9 and
Z
dyn
=
3
the first
T
R
seconds of a video. Therefore, we propose replicating the first
T
R
seconds of each
video in the outermost zones of the disk, thereby taking advantage of the higher transfer rate
of the outermost zones. Assume the first
Z
dyn
zones are used to store the replicated video data,
then the WSGP algorithm will begin pairing zone (
Z
dyn
+
1) and
Z
. Figure 20.4 illustrates the
overall data layout.
20.4.4 An Integrated Scheduler
To support data retrievals for both static and dynamic channels, we devise a new integrated
scheduler based on the three design features previously discussed. The integrated scheduler
is still round-based but each round is divided into two parts - a
static round
and a
dynamic
round
as shown in Figure 20.5. In a static round, two continuous data retrievals are performed,
one for an outer-track block and one for an inner-track block. The retrieved data will then be
used for transmission over the static channels. The dynamic round is further sub-divided into
G
D
dynamic micro-rounds and the dynamic channels are then assigned to these
G
D
dynamic
micro-rounds as in the GSS case. Retrievals within a dynamic micro-round will be executed
using SCAN and the retrieved data will be transmitted over the dynamic channels. The buffer
requirement of this scheduler is thus given by
NQ
(2
N
S
+
N
D
)
(20.4)
as illustrated in Figure 20.6.




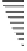














































Search WWH ::

Custom Search