Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
t
t
m
+1
. . .
. . .
Ch x:
Ch x+1:
T
R
<
2
δ
time
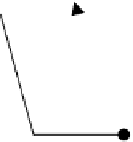
Beginning of a new multicast cycle.
Client starts playback via a static multicast channel.
Request arrives, waits for next multicast cycle.
Figure 19.5
Timing diagram for a statically-admitted client
t
m
t
. . .
Static Ch:
Dynamic Ch:
w
U
time
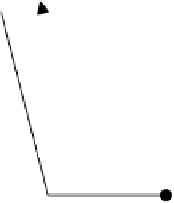
Releases dynamic channel and continues
playback via cached static multicast stream.
A dynamic channel becomes available,
starts playback via dynamic channel.
Request arrives, starts
caching static multicast stream.
Start of a static multicast cycle.
Figure 19.6
Timing diagram for a dynamically-admitted client
from a dynamically-allocated multicast channel. To merge the client back into an existing
static multicast channel, the client concurrently receives and caches video data from a nearby
(in time) static multicast channel as illustrated in the timing diagram in Figure 19.6. Eventu-
ally, playback will reach the point where the cached data began and the client can then release
the dynamic multicast channel. Playback then continues using data received from the static
multicast channel.



































Search WWH ::

Custom Search