Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
5
PB
SB
SB
GDB
: Skyscraper Broadcasting
: Greedy Disk-Conserving
Broadcasting
4
PHB,
m
=1
PHB,
m
=2
PHB,
m
=4
PHB,
m
=16
SDB
PHB
PB
CB
: Staircase Data Broadcasting
: Poly-harmonic Broadcasting
: Pagoda Broadcasting
: Consonant Broadcasting
GDB
6
3
The start- up latency of PHB and CB
converges to the same points
SDB
2
CB,
m
=1
CB,
m
=2
CB,
m
=4
CB,
m
=16
,
1
0
2
b
3
b
4
b
5
b
6
b
Client access bandwidth (multiples of video bit-rate
b
)
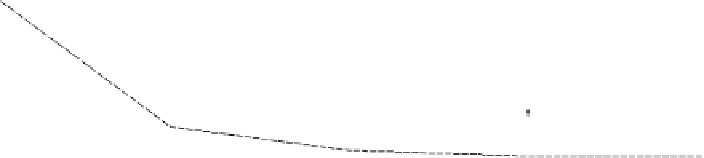
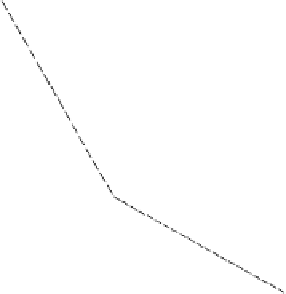
Figure 18.4
Start-up latency versus client access bandwidth (network bandwidth
=
6
b
)
broadcasting schemes require a client access bandwidth to be equal to the network bandwidth.
Therefore, if the client access bandwidth is the bottleneck, the network bandwidth in fact
cannot be fully utilized, leading to the performance degradation.
Finally, we note that the performance of PHB and CB converge when the client access
bandwidth is increased to 6
b
, i.e., same as the network bandwidth, as CB reduces to PHB
when the client access bandwidth constraint is removed.
18.5.3 Client Buffer Requirement
Figure 18.5 plots the maximum client buffer requirement versus the network bandwidth, rang-
ing from 2
b
to 10
b
. The client buffer requirement is normalized and expressed as the ratio of
the size of the media stream. For example, a ratio of 0.3 means that the client buffer must be
large enough to store up to 30% of the whole media stream.
We can observe from Figure 18.5 that the maximum client buffer requirement for all the
schemes are comparable, and varies within a range from 0.2 to 0.5. For example, at a network
bandwidth of 5
b
, themaximumclient buffer requirements are 27%, 43%, 24%, and 32% for SB,
GDB, SDB, and CB (with
m
4) respectively. The only broadcasting scheme that consistently
achieves lower client buffer requirement is SDB. Therefore, the client buffer requirements of
these broadcasting schemes are comparable.
=
18.6 Grouped Consonant Broadcasting
Results in the previous section show that the performance of CB continues to improve for
larger values of the system parameter
m
in equation (18.3). The trade-off, however, is increased




















































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search