Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
New “exceptional” stream,
smoothed using optimal smoothing.
Time
+
Current aggregate bandwidth utilization.
Time
Aggregate bandwidth utilization and reservation
after new stream is admitted.
Bandwidth over-allocated here
to maintain rate monotonicity.
Time
Figure 7.6
Preserving the monotonicity property in the Aggregated MDR scheduler
The monotonicity property of the bandwidth reservation schedule implies that
s
i
+
A
+
v
i
≤
U
⇒
s
i
+
A
+
1
+
v
i
+
1
≤
U
(7.28)
h
g
, and then applying equation (7.28) recursively we can show
that if a new stream's transmission schedule satisfies equation (7.27), the whole transmission
schedule can be added to the bandwidth reservation schedule without exceeding the system
capacity.
The admission test therefore requires (
g
Starting with
i
=
h
0
,
h
1
,...,
+
1) additions and comparisons, instead of the
w
(
g
) additions and comparisons in the original temporal smoothing case. Once the ad-
mission test is successful, then the new stream's transmission schedule will be added to the
aggregate system utilization using equation (7.25) and then the system can compute the new
bandwidth reservation schedule according to equation (7.26).
Assume a proportion of
w>>
1) of the video collection can be admitted using MDR
schedules under a given client buffer size constraint. Then, for successful admissions, the
admission complexity is equal to O(1
α
(0
≤
α
≤
) additions.
For unsuccessful admissions, again the complexity will be lower as the admission test is
stopped as soon as the system utilization is exceeded in a time slot.
+
(1
−
α
)(
g
+
w
)) comparisons and O(
w

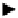
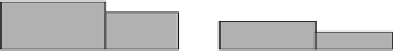






















Search WWH ::

Custom Search