Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
fluctuation caused by Brownian agitation of the molecules increases
the concentration of
Ac
, its activator effect at this point becomes
greater than the inhibitor effect of
I
. If, in addition, this fluctuation
is sufficiently great, the system will not return to its initial state.
The autoactivator effect of
Ac
on its own synthesis is increased at
the same time as activation of the synthesis of
I
. The result is an
concentration of A and I
Ac
Ac
I
I
A
B
K
position on an
axis of the embryo
Ac
Ac
I
I
C
D
K
K
E
K
F
IGURE
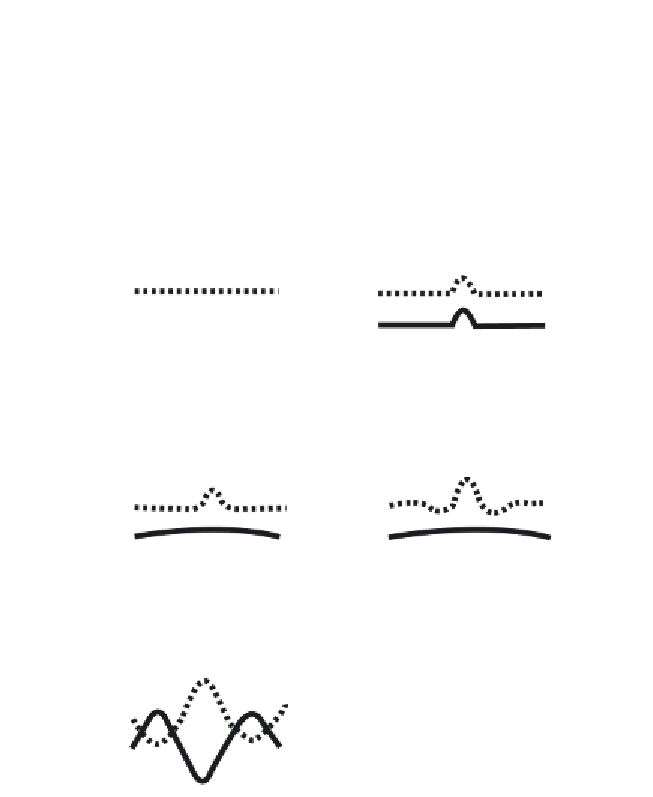
3. The reaction-diffusion mechanism. A:
The activator
Ac
(dotted line)
and the inhibitor
I
(solid line) are in equilibrium, in a homogeneous concentra-
tion in an embryo.
B:
This system is disturbed at a point
k
. The result is local
fluctuation of the concentrations of
Ac
and
I
.
C:
The disturbance of
I
is propa-
gated more quickly than that of
Ac
.
D:
Consequently, at certain points the
inhibitor effect of
I
becomes greater than the activator effect of
Ac
. This results
in reduction in the concentration of
Ac
.
E:
This effect increases until the system
reaches a new heterogeneous equilibrium.