Biology Reference
In-Depth Information
repression
a
b
activation of
gene cluster b
(phenotype B)
activation of
gene cluster aa
(phenotype A)
repression
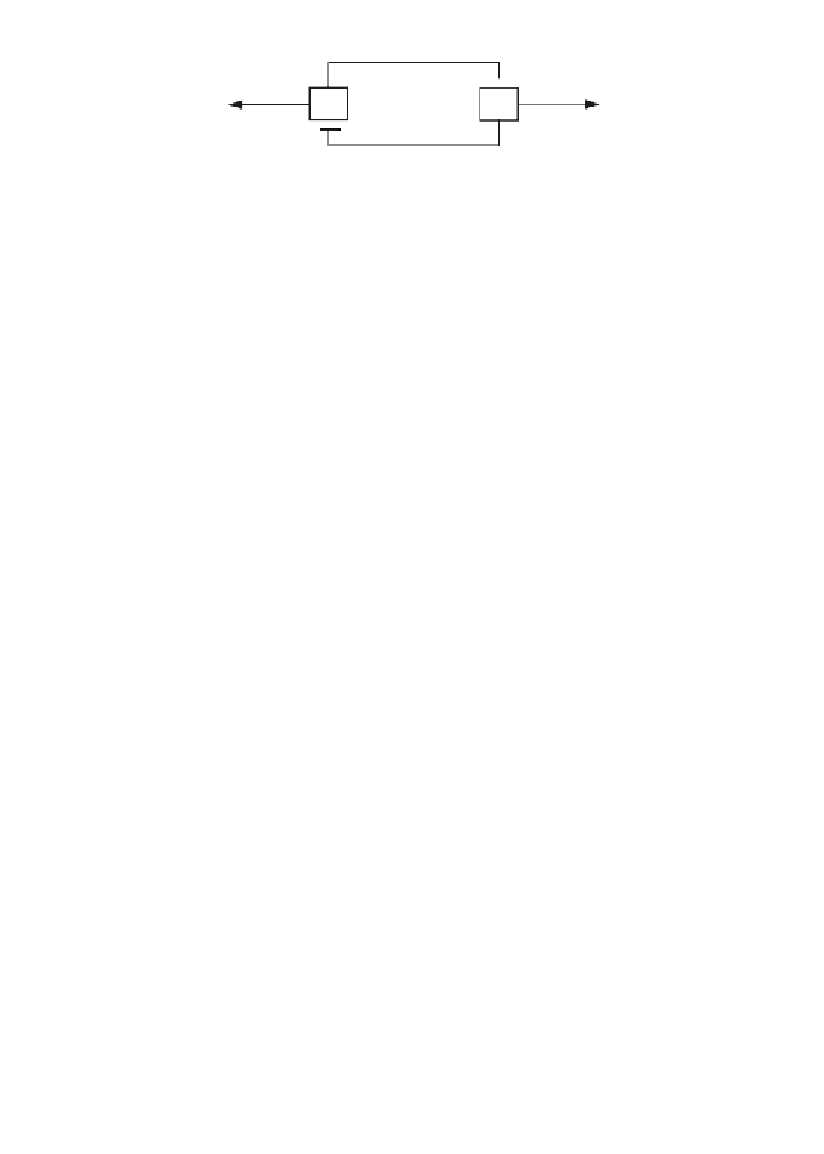
F
IGURE
28. Bistability of a network of genes.
Two genes mutually repress each
other in the same cell. Gene
a
represses gene
b
and gene
b
represses gene
a
.
Fluctuation in this network which increases the activity of one of these two genes
to the detriment of the other augments until the latter gene is totally repressed
and the former activated. As fluctuations are inevitable and can be randomly
produced in favour of one or other of the two genes, some of the cells in a popula-
tion will bifurcate towards type A (corresponding to activation of
a
) and others
towards type B (corresponding to activation of
b
).
those involved in gene expression (chapter 4). This does not mean
that all the work done in this theoretical context is wrong but that
another, much more important source of randomness must be
added to it, due to the combination possibilities ensuing from the
non-specificity of chromatin molecules.
6.5.2
Self-organisation model of chromatin
According to the second interpretation of the stochastic expression
of genes, the architecture of chromatin and the cell nucleus is
thought to arise through a process of self-organisation involving ran-
dom modifications of their structure. This process occurs sponta-
neously due to local interactions between the chromatin molecules,
and tends towards the thermodynamic state of maximum equilib-
rium (Dundr and Misteli, 2001; Misteli, 2007; de Laat and Grosveld,
2007). Adherents to this conception try to justify it using a great
deal of data obtained recently using the most sophisticated tech-
niques. These data reveal cell nucleus properties which at first sight
seem paradoxical. The nucleus is both extremely structured and
extremely dynamic. Each chromosome is organised in a territory
specific to it, which means that the genes are precisely positioned in
the three-dimensional nuclear space. Genes co-expressed in one cell