Geology Reference
In-Depth Information
cf. Fig. 2.4
CaMgSi
2
O
6
diopside
1392°C
10
90
An
b
Di
20
80
13
50
cf. Fig. 2.5
Ab
30
70
40
a
1274°C
Diopside
crystallises
first
50
50
60
40
1250
70
30
b
80
1200
20
Plagioclase
ss
crystallises first
1133°C
10
1553°C
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
NaAlSi
3
O
8
albite
CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
anorthite
Mass percent CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
(c)
(d)
CaMgSi
2
O
6
(Di)
1220°C
b
c
Di
An
Di + Plag
ss
+ melt
Ab
Di + melt
d
Di + Plag
ss
b
melt
c
CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
(An)
NaAlSi
3
O
8
(Ab)
Plag
ss
+ melt
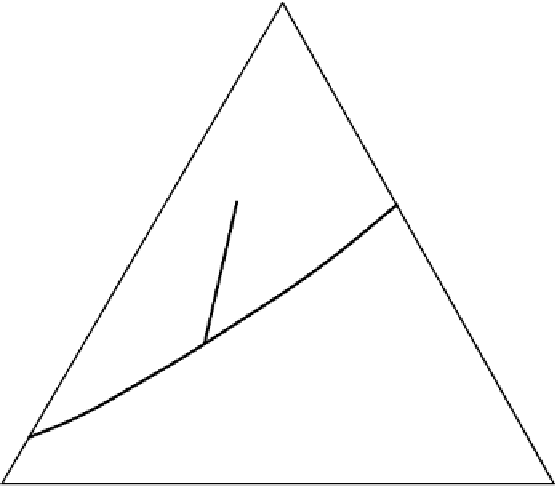
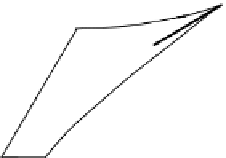
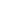
Figure 2.9
Various ways of representing crystallization in the
pseudo-ternary
system CaMgSi
2
O
6
-NaAlSi
3
O
8
-CaAl
2
Si
2
O
8
. (a)
A perspective sketch of the liquidus surface in three dimensions. Elevation and contours represent temperature. (b) A plan
view of the liquidus surface, with topography shown by temperature contours (graduated in °C). (c) 3D sketch indicating the
construction of the isothermal section shown in (d). (d) Isothermal section at 1220 °C. Tie-lines across the two-phase fields
link coexisting phase compositions. The arrow (a tangent to the
cotectic
curve in Figure 2.9b) indicates the direction in which
the melt composition
b
will evolve with further crystallization. This direction is controlled by the proportion in which
diopside and plagioclase
c
crystallize (point
d
).










































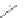





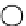




























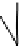














































Search WWH ::

Custom Search