Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
the decision is taken on all the hypotheses except
D
(in favor of the hypothesis
C
1
∪
C
3
for the ALD branches, respectively). With this decision rule, there is practically no dif-
ference in the decision images, showing the robustness with respect to weighting. This
supports the idea that composite hypotheses should not be so often ignored.
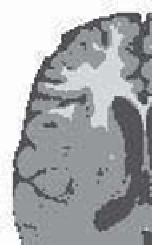
Figure 7.4.
Decision by maximum belief based on simple hypotheses,
for an increasing weight on
m
2
(
C
3
)
and
m
1
(
C
2
)
Let us now examine the influence of overall absence of knowledge, modeled by a
mass on
D
added by discounting, according to reliability coefficients for each source.
This time, the result of the combination
m
1
⊕
m
2
is no longer a Bayesian mass function
and the decision by maximum belief is no longer equivalent to the maximum plausibil-
ity. In fact, we do observe small differences in the decision images. We have observed
only very slight differences when the decision is made based on simple hypotheses.
However, decisions on all of the hypotheses except
D
are always made in favor of a
composite hypothesis, as expected. In our application, there is no particular argument
for suggesting that one image is more or less reliable than another (overall because
this is not true on a class per class basis). This is why it is not very useful to assign a
mass to
m
(
D
) and this is confirmed by the results. On the other hand, we have strong
arguments to support partial absence of knowledge, depending on the image, which
leads to ambiguities between classes and this was included by masses for the com-
posite hypotheses. Once again, this justifies the method used for assigning masses,
which relies on how the problem is modeled, rather than the traditional method based
on probabilities and overall reliability factors.
The images used in this example were acquired with rather thick sections, thus
causing a strong partial volume effect, particularly between white matter and the ALD
(see Figure 7.1). We will now include this knowledge explicitly as a mass on
C
1
∪
C
3
in the second image (trapezoidal function inferred from the histogram). This reduces
conflict. The combination
m
1
⊕
m
2
is no longer a Bayesian mass function and the
decision areas are modified, as shown in Figure 7.5.


Search WWH ::

Custom Search