Image Processing Reference
In-Depth Information
any
C
i
∈
Bel(
A
), a certain number of precautions have
to be taken in order to decide in favor of a composite hypothesis. We can, for exam-
ple, imagine making a decision in favor of a composite hypothesis if the arguments
involving the simple hypotheses are not strong enough.
A
and because Bel(
D
)
≥
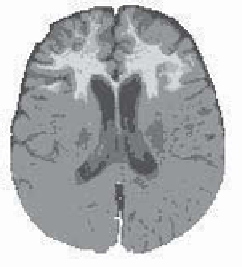
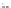
Thus, in Figure 7.2, the decision was made according to the maximum belief over
all of the hypotheses except
D
. Let us note that, in this simple case, the maximum
credibility is equivalent to the maximum plausibility, since
m
1
⊕
m
2
is a Bayesian
mass function. With this rule, the decision is made in favor of a simple hypothesis in
the points where other masses are equal to zero and in favor of a composite hypothesis
otherwise. This way, we obtain interesting results since the partial volume points are
detected as a composite hypothesis, whereas the areas without ambiguity are well
segmented. Figure 7.3 shows the results obtained by making a decision in favor of a
simple hypothesis with the maximum belief.
C3
C2
C2 U C3
C1 U C3
C1 U C2
C1
C1 (brain)
C2 (ventricles + CSF)
C3 (ALD)
C1 U C2
C1 U C3
C2 U C3
Figure 7.2.
The different decision areas depending on the values of
m
2
(
C
3
)
and the decision image, by taking the maximum belief over all of the hypotheses except
m
1
(
C
2
)
and
D


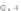






































Search WWH ::

Custom Search