Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Table 2.3
Comparison of the
prediction RMSE for
validation data
EKF(c)
EKF
(
c
+
a
)
v
(
t
+
6
)
0
.
0094
0
.
0091
v
(
t
+
12
)
0
.
0058
0
.
0045
v
(
t
+
85
)
0
.
0810
0
.
0767
1.5
v
(
t
+6)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
1.5
v
(
t
+12)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
1.5
v
(
t
+85)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
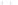
Fig. 2.16
Model training in prediction 6, 12 and 85 steps ahead of Mackey Glass chaotic time
series
1.5
v
(
t
+6)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
1.5
v
(
t
+12)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
1.5
v
(
t
+85)
EKF(c)
EKF(c+a)
1
0.5
0
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
500
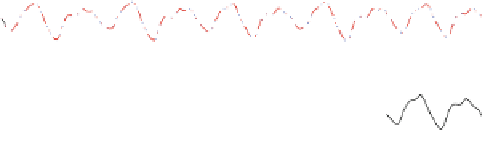
Fig. 2.17
Model validation in prediction 6, 12 and 85 steps ahead
10
12
covariance matrix is initialized as
α
=
1,000 for EKF(c) algorithm, and
α
=
9
×
10
−
6
for EKF
and
algorithm.
The results of the execution of the two algorithm are shown in Table
2.3
.
Figures
2.16
and
2.17
show the Mackey Glass chaotic series and the predictions
for training and validation data respectively.
β
=
(
c
+
a
)



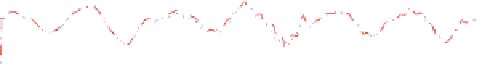




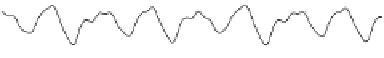
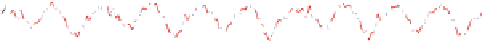






































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search