Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 14.5
Torque-speed
curve
of the motor
where
J
e
is the inertia of the motor,
ω
e
its angular speed, which is the same as
the pump of the torque converter,
T
e
the torque due to the combustion, and
T
p
the
resistant torque from the pump of the torque converter.
The maximum torque delivered by the motor (
T
max
) is obtained from its torque-
speed curve, which is modelled as a second order polynomial of its speed, as is shown
in Fig.
14.5
. The actual torque (
T
e
) is a fraction of that maximum torque, proportional
to the action on the accelerator pedal (
ac
):
T
e
=
.
0
01
ac T
max
(14.16)
For the torque converter, an experimentally obtained staticmodel is used (Kotwicki
1982
). If
T
p
,
T
t
,
ω
t
are the torques and speeds in the pump and the turbine
respectively, the model provides the torques as functions of the speeds:
ω
e
and
ω
t
<
0
.
9
ω
e
10
−
3
2
10
−
3
10
−
3
2
t
T
p
=
3
.
4325
·
ω
e
+
2
.
221
·
ω
e
ω
t
−
4
.
6041
·
ω
10
−
3
2
10
−
3
10
−
3
2
t
T
t
=
5
.
7656
·
ω
e
+
0
.
3107
·
ω
e
ω
t
−
5
.
4323
·
ω
ω
t
≥
0
.
9
ω
e
10
−
3
2
10
−
3
10
−
3
2
t
(14.17)
T
t
=
T
p
=−
6
.
7644
·
ω
e
+
32
.
0024
·
ω
e
ω
t
−
25
.
2441
·
ω
The torque in the turbine is amplified by the gear ratio in the gearbox, which is
modelled as a map that relates the moment of the change of gear with the wheel
speed and the throttle position, as in Fig.
14.6
. The gear ratios used are 3.56, 2.19,
1.41, 1.0 and 0.83 from first to fifth gear respectively.



















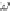







































Search WWH ::

Custom Search