Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
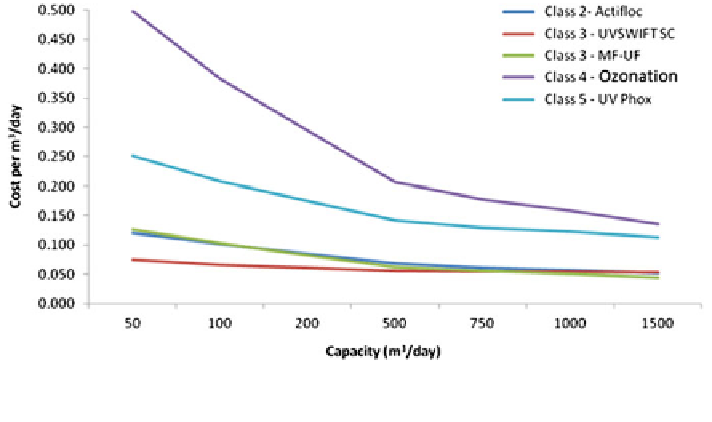
Fig. 3.3 Estimated cost curves: Class 2 for HRC, Class 3 for UV and MF-UF, Class 4 for
Ozonation and Class 5 for a UV-based AOP
additional costs must be added for suspended solid removal, such as sand
filtration,
which could add up to 5 cents per cubic meter, and has been included in Table
3.4
and in Fig.
3.3
. Ozonation seems to be the most expensive, but of course it can
remove more contaminants and goes beyond disinfection. Perhaps this jump in the
classes is a nonlinear feature, and therefore the cost per cubic meter increases by an
anomalous amount from Class 3 to Class 4.
Ozone treatment plants
6
have expanded rapidly in small systems across
Saskatchewan and Manitoba in Canada, mostly for surface water sources. By one
count, there were about 30 small ozone plants in operation (at the end of 2010).
Compared to a UV-based treatment plant, ozonation is more expensive, but nev-
ertheless it is proving to be attractive to a number of smaller communities.
3.4 Class 5 Treatment Technologies
UV-based advanced oxidation process (AOP) is classi
ed as a Class 5 treatment
technology in Table
3.1
. Hydrogen peroxide absorbs UV light in order to form free
hydroxyl radicals, which aid in breaking down contaminants. A combination of
UV-photolysis and UV
Oxidation is therefore used in the treatment process. In
Table
3.5
we present the estimated NLLS average cost function for such an AOP.
-
6
These Ozone treatment plants were supplied by Mainstream water solutions Inc. Their brand
name was SCOR.
Search WWH ::

Custom Search