Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
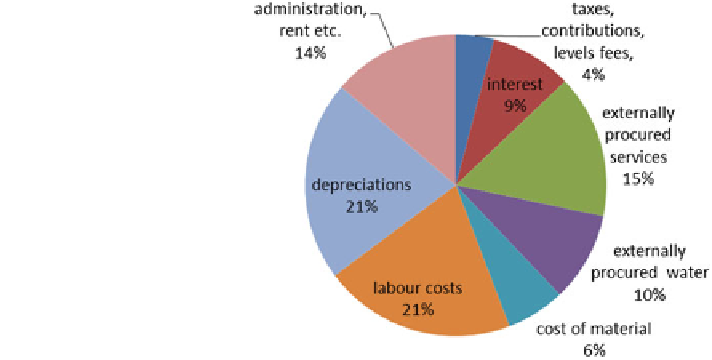
Fig. 12.7 Cost structure in
water supply in 2004 (Althoff
2007
)
d. Adequate interest yield for equity capital and debt capital. In order to ensure
long-lasting security of water supply, water supply utilities should obtain a pro
t
that allows at least a current market rate of interest on the capital invested.
8
e. Adequate maintenance of the capital infrastructure. For long-term security of
supply, there must be adequate provision for the maintenance and renewal of
capital equipment. The municipal water supply system generally has a long
service life of 20 years and up to 70 years for pipelines and hydrants. Moreover,
after the service life, the replacement of equipment must be based on expected
future prices and not the historical prices of the old equipment.
12.6.2 Wastewater Disposal
In Germany, the freshwater standard and the split charge standard are two ways of
calculating wastewater charges. The main difference between the two methods is
that the cost for rainwater collected from public property is separated and its cost is
divided equally over the community. On the other hand the cost of rainwater
collected from private property is charged to the owner of the property.
The freshwater standard assumes that the amount of freshwater used by an
owner ends up eventually as wastewater. So that is the
first component of the total
wastewater charge paid for by the private owner. The second component is then
based on the amount of rainwater collected and processed from streets and from
public property, which is called the split charge. Most large municipalities are able
8
This corresponds with the principles of economic activity of municipalities that are stated in the
municipal bylaws of the federal states (Althoff
2007
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search