Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
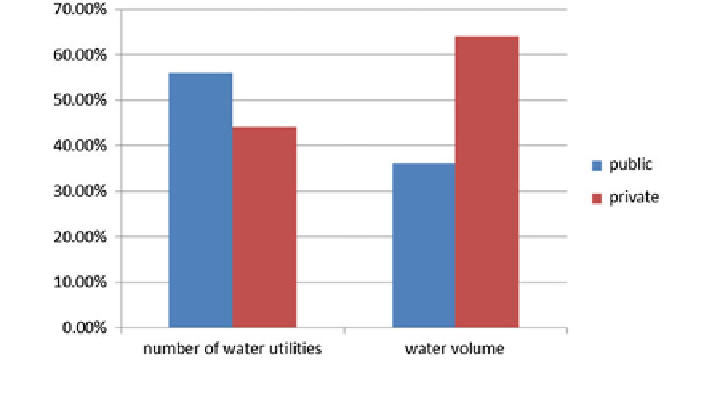
Fig. 12.1 Companies for public water supply in 2008 (Reproduced from ATT et al.
2011
)
As a result, according to the Federal Ministry for the Environment, the quality of
drinking water in Germany is very good. More than 91 percent of customers are
extremely satis
ed or satis
ed with the water quality (ATT et al.
2011
).
12.2.2 Groundwater and Surface Water Bodies in Germany
Groundwater reserves are the most important source of drinking water. Roughly
74 percent of drinking water is drawn from ground and spring water, and the
remainder is drawn from surface water sources, such as lakes and rivers Althoff
(
2007
). Article 7 of the EC Water Framework Directive requires that
“
member
states shall ensure the necessary protection for the bodies of water identi
ed with
the aim of avoiding deterioration in their quality in order to reduce the level of
puri
”
Moreover, the
objective of Article 8 of the EC Water Framework Directive is to achieve a
cation treatment required in the production of drinking water.
“
good
ecological and chemical condition
good quantitative and
chemical condition
”
of groundwater by 2015.
1
In Germany, the L
ä
nder are
responsible for implementing water legislation and water protection measures for all
water including groundwater. All source waters are monitored through a compre-
hensive monitoring network to test for contamination under the Federal Water Act.
By 2010, 63 percent of the groundwater bodies in Germany had achieved a
rating of
”
of surface water and a
“
(BMU
2014
). Of the total 1,000 groundwater
bodies, only 4 percent have not achieved a
“
good chemical status
”
“
good quantitative status,
”
i.e. 4 percent
1
The regulations set out in the European Water Framework Directive have been incorporated into
German law with the Federal Water Act (BMU
2014
).
Search WWH ::

Custom Search