Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Cut-off of riparian lakes from the Yangtze River stressed the complex ecosystem in the lakes and the
river. Figure 10.26 shows a comparison of species richness of aquatic plants and benthic invertebrates in
isolated lakes and river-linked lakes in the middle and lower Yangtze River basin (Wang and Wang,
2008). The connection of the isolated lakes with the Yangtze River was cut off in the past decades, which
has resulted in continuous reduction of species. The cut-off also caused reduction of fish species. There
are 101 fish species in the river-linked Poyang Lake but only 57 and 47 fish species in the isolated Honghu
Lake and Zhangdu Lake.
An experiment was conducted in the Juma River in the suburbs of Beijing. In a backwater area of the
river two experimental plots, a large one with area of 100 m
2
and a small one with area of 4 m
2
, were
separated from the neighboring water by steel sheet walls. The impact on benthic invertebrates was
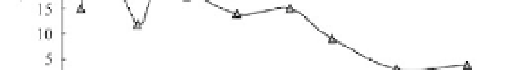
monitored for 6 months. Figure 10.27 shows the variation of the total abundance and species richness in
the two plots compared with those of the open water. In the first 40 days the differences between the
three kinds of habitats are inconsistent. Nevertheless, it becomes clear after 40 days that both abundance
and species number in the closed plots reduced greatly. The abundance and richness in the small plot
Fig. 10.26
Comparison of species richness of aquatic plants and benthic invertebrates in isolated lakes and river-linked
lakes in the middle and lower Yangtze River basin (after Wang and Wang, 2008)
Fig. 10.27
The number density,
N
, and species number,
S
, of benthic invertebrates in fragmented habitats (large
plot area 100 m
2
; small plot area 4 m
2
) varying with time (after Duan and Wang, 2008)
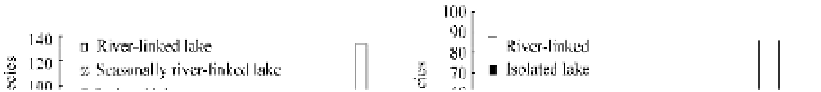









Search WWH ::

Custom Search