Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
treatment plants either directly or through its tributaries. In the 1970s and 1980s, these wastewater
treatment plants operated as standard secondary treatment plants removing CBOD, but not ammonia. By
the 1990s most of the plants applied nitrification to remove ammonia loads to Salt Creek.
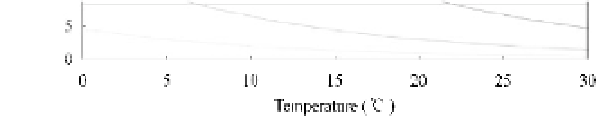
Fig. 9.19
Comparison of U.S. Environmental Protection Agency acute toxicity standard (Criterion Maximum
Concentration, CMC) and the former Illinois un-ionized ammonia standard converted to total ammonia concentration
In Illinois the quality of the macroinvertebrate community in a stream is measured by the Macroinvertebrate
Biotic Index, MBI (IEPA, 1987), which is a variation of the Hilsenhoff (1987) Biotic Index. The MBI is
computed as follows:
m
¦
MBI
(
nt
) /
N
(9.35)
ii
i
1
where
n
i
is the number of individuals in each taxon,
t
i
is the tolerance rating assigned to each taxon,
N
is
the total number of individuals in the sample, and
m
is the number of taxons. The MBI ratings are as
follows: < 5 is very good; 5-5.9 is good; 6-7.5 is fair; 7.6-9 is poor; and
ı
9 is very poor. Figure 9.20
shows the changes in the MBI value over time for five sampling locations on Salt Creek. Station GL-10
is near the upstream boundary of the study reach and is minimally impacted by wastewater treatment plant
effluent, hence the good to fair ratings at all times. Station GL-16 is at the confluence of Salt Creek and
one of its major tributaries and is downstream from 3 wastewater treatment plants, hence it fair rating at all
times. Stations GL-04 and GL-02 are downstream from 8 and 10 wastewater treatment plants, respectively,
leading to the very poor ratings in 1975 and poor and fair ratings, respectively, in 1983. However, in 1995
once all of these plants applied nitrification and ammonia toxicity decreased the ratings moved into the
good range. Station GL-09 is 14.3 km downstream from GL-02 and more than 17 km downstream from
the last wastewater treatment plant. Thus, the fair ratings in 1975 and 1983 reflect the natural conversion
of ammonia to nitrate (and consequent decreases in ammonia toxicity) as the water flows from GL-02 to
GL-09, and the good rating in 1995 reflects both in-wastewater treatment plant and natural nitrification.
9.3.2
Nutrient Control
9.3.2.1
Best Management Practices (BMPs)
The primary sources of nutrients in surface waters are diffuse/non-point sources. For example, Goolsby
and Battaglin (2000) reported that only 11% of the total nitrogen in the Mississippi River came from






Search WWH ::

Custom Search