Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
1.2
Major River Management Issues
1.2.1
Water Resources
Water resources refer to available or possibly available water sources that possess adequate quantity and
utilizable quality and may be utilized in a specific location for a specific purpose. Only the available water
sources (such as river runoff) and waters in water bodies either on the surface or in groundwater aquifers,
which take part in hydrological cycle activities, are considered and counted for quantitative statistics.
China has enormous water resources but they are unevenly distributed in space and in time. In per capita
terms, China's water resources are about 75% of the Asian average, and 35% of the world average. The
total volume of annual runoff is 2.7 trillion m
3
, equivalent to about 45% of the precipitation corresponding
to a depth of 284 mm over the land area. About 65% of the country's territory lies in catchments of rivers
flowing to the sea, and 35% in inland, landlocked basins. About 27% of natural runoff flows into
neighboring countries, mainly in the southwest and the northeast boundary rivers. The Ertix River in the
far northwest flows north to join the Ob River in Siberia. About 0.6% of the total runoff flows into China
from other countries. Glaciers store about 5.1 trillion m
3
. Annual melt-water is about 2% of the combined
discharge of the inland rivers. Groundwater recharge is about 0.83 trillion m
3
although most of this
represents water transformed into river flows under natural conditions and is thus already accounted for
by river runoff. Excluding such double counting, the net total water available (surface water plus
groundwater) is 2.8 trillion m
3
, and the net additional contribution of groundwater is about 0.1 trillion m
3
.
This is mainly rainfall infiltration on the plains since groundwater in mountainous areas is almost wholly
accounted for in base flows which are included in river flows.
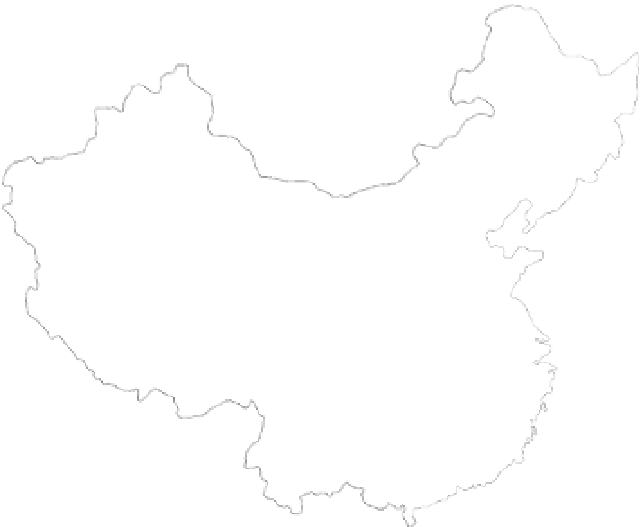
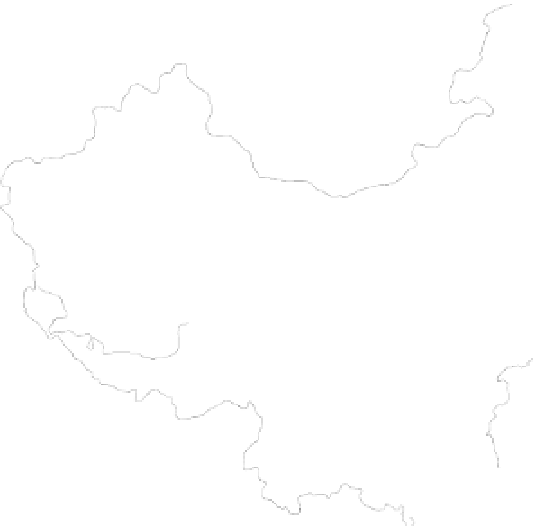
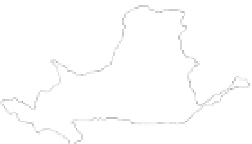
The water resources distribution in China is very non-uniform, with the south-east of the country wet
and north-west dry. Figure 1.23 shows the 10 water resources zones of China and the inflow and outflow
of moisture across the north, east, south, and west borders. The main moisture supply is from the south of
Heilongjiang
River Basin
23%
15%
Liaohe
River Basin
Haihe
River
Basin
Continental Basin
23%
12%
Yellow River Basin
Huaihe
River Basin
10%
60%
Southwest Basin
Zhe
Min
Tai
Basin
Yangtze River Basin
Zhujiang River Basin
15%
42%
Fig. 1.23
Inflow and outflow of moisture to China and the 10 water resources zones of China





















Search WWH ::

Custom Search