Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
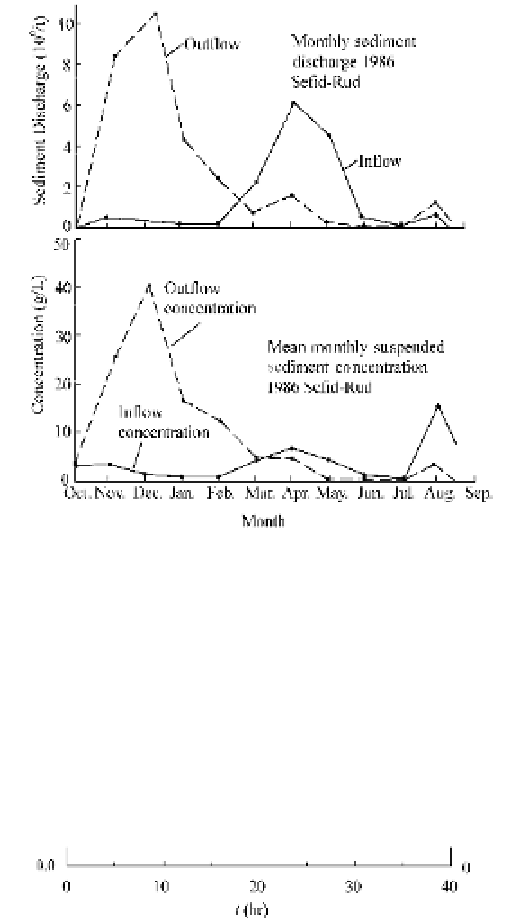
Fig. 7.12
Sediment discharge and sediment concentration of the inflow and outflow of the Sefid-Rud Reservoir in
Iran during the empty flushing (after Forood and Ghafouiri, 2007)
Fig. 7.13
Sediment concentration and discharge of mud flow during the empty flushing from the Hengshan Reservoir
in 1979 (Data from Guo et al., 1985)
The Zhuwo Dam is on the Yongding River near Beijing, China, which is 33 m high with a reservoir
capacity of 14.75 million m
3
. The reservoir began to store water in 1961 and lost 5.3 million m
3
of
reservoir capacity due to sedimentation after 25 years of operation. Most of the sediment deposit was
cohesive sediment with a median diameter of 0.004 mm. A physical model experiment was conducted to
study the efficiency of empty flushing of cohesive sediment from the reservoir (Wang and Zhang, 1989).
Cohesive sediment may be carried downstream if the sediment is scoured from the reservoir. Figure 7.14
shows the critical velocity,
U
c
, for initial scouring of cohesive sediment from the reservoir as a function
of the weight of sediment per unit volume in the deposit,
J , which followed the following formula:
(7.1)
Because the length and depth scale of the model was 1:50 then the velocity scale can be calculated
from the Froude Number to be 1:7.07. The scale ratio for the critical velocity for scouring similarity is
U
4.6
J
4
c
b




Search WWH ::

Custom Search