Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
of the reservoir. In the first 8 years of the reservoir impoundment, coarse sediment will be trapped and
clear water will be released to the lower reaches. It was calculated that 0.3 billion tons of sediment in the
lower reaches channel will be scoured by the released clear water and transported to the ocean. The
reservoir will be operated so as to trap coarse sediment and discharge fine sediment. Most of the fine
sediment will be released with water discharges over 2,000 m
3
/s or more. The sediment load will vary
and can be roughly calculated as the incoming sediment load into the reservoir minus the fraction trapped
in the reservoir, plus the scoured sediment from the lower reaches channel and the incoming sediment
from the catchment below the reservoir. Most of the sediment load will be transported during the flood
season and the sediment load transported will be more concentrated during floods.
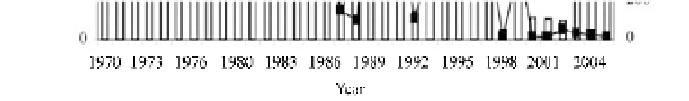
Fig. 6.16
Variation of water and sediment load at the Lijin Station in the lower Yellow River from 1970-2005
Because the coarse fraction of sediment is trapped by the reservoir, the rate of sedimentation of the
lower Yellow River channel will be greatly reduced. According to numerical models, the Xiaolangdi
Reservoir may control sedimentation of the lower Yellow River for more than 20 years. Nevertheless, the
fine sediment will be released into the lower Yellow River to reduce the rate of sedimentation of the
reservoir. Sediment finer than 0.02 mm in the river is mostly wash load and can be transported into the sea.
On July 4, 2002 the first experiment of an artificial flood created with the Xiaolangdi Reservoir was
conducted to explore the possibility of scouring the lower Yellow River bed. The flood of peak discharge
of about 2600 m
3
/s was released from the reservoir and maintained about ten days. Figure 6.17 shows the
Fig. 6.17
Artificial flood created by releasing water from the Xiaolangdi Reservoir on July 04, 2002. Water was
released from different elevations to control the sediment concentration. The released concentration from the bottom
outlet is high dying the water yellow and red, and the water from the top outlet is clean and white







Search WWH ::

Custom Search