Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
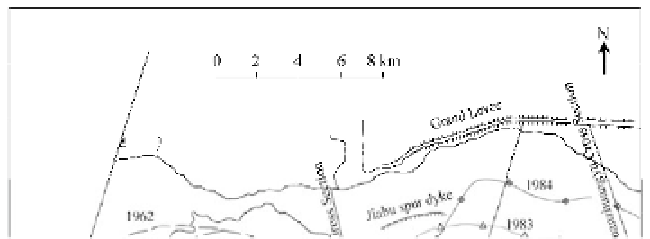
Fig. 1.16
Wandering channel of the lower Yellow River during the periods 1960-1964 and 1981-1985. The high speed
of migration of the channel can be seen by identifying the curves of the channels of the consecutive years
Northeast China. On the flat plane land the river bifurcates into two or more channels and merge again
after traveling a long distance. The characteristics of the river are in accordance with the description of
Smith and Smith (1980).
Fig. 1.17
Anastomosing channels of the Mudanjiang River in Northeast China (Satellite image from the Google Earth)
1.1.6
Morphological and Hydraulic Features
Channel slope
—Channel slope or gradient is measured as the difference in elevation between two points
in the stream divided by the stream length between the two points. Channel slope directly impacts flow
velocity, shear stress, and stream power. Since these attributes drive the geomorphic processes of erosion,
sediment transport, and sediment deposition, channel slope becomes a controlling factor for channel
shape and pattern.
Knickpoint
is a term to describe a location in a river or channel where there is a sharp change in







Search WWH ::

Custom Search