Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Landslides also are classified according to their scale into: huge landslides with a volume of sliding
material over 10
8
m
3
, large scale landslides with volume between 10
6
m
3
and 10
8
m
3
, middle scale landslide
with volume between 10
4
m
3
and 10
6
m
3
, and small scale landslides with a volume less than 10
4
m
3
. Rockfalls
are usually in the small scale, and avalanches and rockslides are in the middle and small scales. Only the
translational and rotational landslides are in the large and huge scales.
Landslides are also classified according to their causes into earthquake landslides, rainstorm landslides,
congelifraction avalanches, liquefaction landslides, reservoir-induced landslides, highway landslides, and
mining landslides. Rainfall induced landslides occur widely in hilly and mountainous areas. According to
the water content of the sliding body, landslides are classified into dry landslides, unsaturated landslide,
and saturated landslides. Landslides also are classified by materials into rock landslides, semi-solid
landslides, and soil landslides.
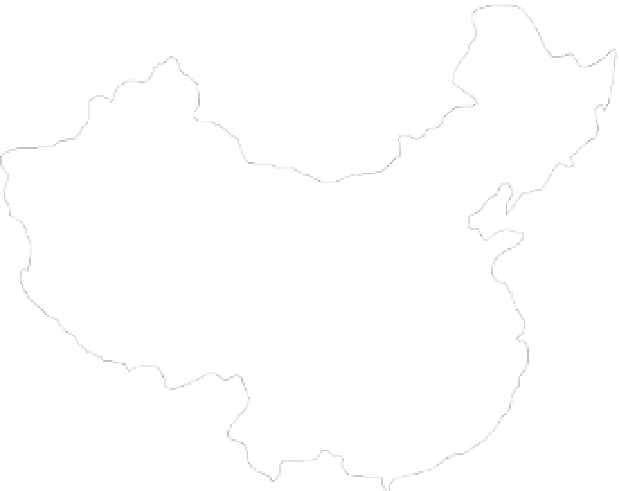
China is a country with a vast territory of mountains. Landslides and avalanches occur throughout the
mountainous areas. Figure 4.3 shows the distribution of landslides and debris flows in China (NFH and
IMH, 1994), in which the different shadowed areas are debris flow areas with different types of debris
flows and the locations of black points are the sites of landslides. Frequent and disastrous landslides
occur in areas with active tectonic and stream erosion areas. These areas cover two thirds of the
mountainous areas of China, especially northwestern and southwestern China. Many landslides have
occurred along the upper reaches of the Yangtze River and at the edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
Harbin
Urumqi
Site of land slide
Hohhot
Beijing
Mud flow
Landslide
Lands lide
Rainfall debris flow
Glacial debris flow
Zhengzhou
Hefei
Mud flow
Glacial debris flow
Lhasa
Shanghai
Chengdu
Yangtze River
Rainfall debris flow
Rainfall debris flow
0
250
500
750 km
Fig. 4.3
Distribution of landslides and debris flows in China (The different shadowed areas are debris flow areas with
different types of debris flows and the locations of black points are the sites of landslides) (after NFH and IMH, 1994)
Huge and large scale landslides are triggered by earthquakes or rainstorms. But some small scale
landslides result from human activities, such as disposal of mining debris, deforestation, and construction
on slopes. Swanston (1999) analyzed the relation between landslides and timber harvest. Forest harvest
operations in southeastern Alaska have influenced both the frequency and size of landslide events.
Southeastern Alaska is characterized by naturally steep slopes, shallow soils, and a thick, old-growth
forest cover. Precipitation ranges from 1,524 and 5,080 mm a year. Because of high soil permeability,





































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search