Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Fig. 3.4
A broken bridge illustrating the lateral tilt of the river valleys caused by the 921 earthquake in Taiwan
(September 21, 1999)
The streams in the area are incised channels and the bank slopes are so steep that slope failures readily
occur during rainstorm and earthquake events. The rising plateau has increased the gradient of rivers and
caused dramatic changes to stream networks. In general the rivers flows from northwest to southeast are
strengthened and extended but the rivers in an opposite direction are reduced in length or eliminated.
Asymmetry of stream networks is then evident in watersheds on the margin of the plateau. Figure 3.5
shows the stream network of the Xihanshui River (the upstream area of the Jialing River) on the
northeastern margin of the plateau. All large tributaries join the river from the northwestern side, creating
a very asymmetrical stream network. More than 90% of the drainage area is on the western side of the
river. This situation is repeated for many stream networks at the margins of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau.
Fig. 3.5
Asymmetrical distribution of tributaries and drainage area of the Xihanshui River
3.1.2.2
Geomorphic Causes
Geomorphic causes of incision for the most part involve an increase in gradient. For example, stream
capture, base-level lowering, meander cutoffs, avulsion, cliff retreat, sediment storage, and lateral shift of





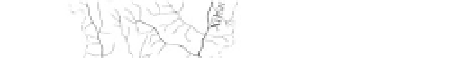




Search WWH ::

Custom Search