Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
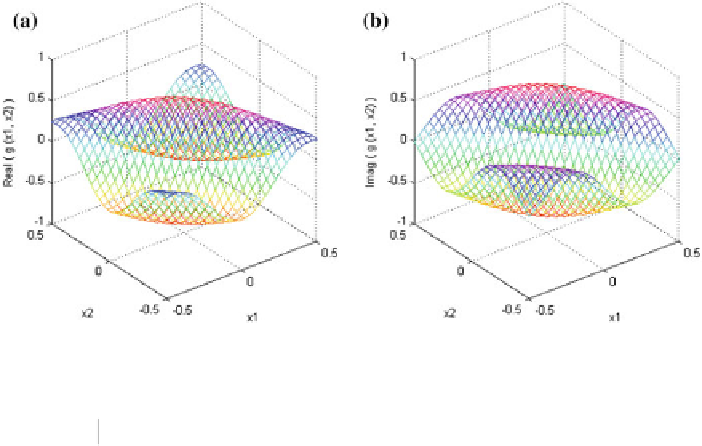
Fig. 4.2
2D Gabor function;
a
real part and
b
imaginary part
Table 4.4
Comparison of training and testing performance for 2D Gabor Function
C
MLP
C
RPN (
d
=
0
.
96)
C
RSS
C
RSP
Algorithm
C
BP
C
RPROP
C
BP
C
RPROP
C
BP
C
RPROP
C
BP
C
RPROP
Network
2-10-1
2-10-1
2-10-1
2-10-1
2-5-1
2-5-1
2-5-1
2-5-1
Parameters
41
41
41
41
41
41
41
41
MSE
0
.
0018 0
.
00088
0
.
0026 0
.
00091
0
.
001
0
.
00097
0
.
00069 0
.
0004
(training)
MSE
0
.
0039 0
.
0016
0
.
0048 0
.
0017
0
.
0019 0
.
00099
0
.
0011
0
.
00062
(testing)
Correlation
0
.
9816 0
.
9913
0
.
9886 0
.
9958
0
.
9954 0
.
9976
0
.
9978
0
.
9979
Error
0
.
0039 0
.
0021
0
.
0046 0
.
0017
0
.
0019 0
.
00079
0
.
0011
0
.
00063
variance
AIC
−
6.18
−
6.73
−
5.78
−
6.82
−
6.67
−
7.32
−
7.27
−
7.76
Average
9,000
2,000
9,000
2,000
9,000
2,000
9,000
2,000
epochs
test set. For comparison, we tried the approximation of above function with different
networks using two training algorithms viz
C
BP (
01) and
C
RPROP
μ
−
=
ʷ
=
0
.
1
. After experimenting
with different numbers of hidden neurons and training epochs, the best result is
reported in Table
4.4
. In order to graphically visualize the 2-D Gabor function, the
real and imaginary part of different network's outputs are shown in Fig.
4.3
. Results
in Table
4.4
clearly demonstrate that the
C
RSP network with
C
RPROP perform best
with least error variance and testing error in only 2000 epochs, keeping same number
of learning parameters.
,μ
+
10
(
−
6
)
,ʔ
max
0
.
5
=
1
.
2
,ʔ
min
=
=
0
.
1
,ʔ
0
=
0
.









































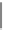











































Search WWH ::

Custom Search