Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
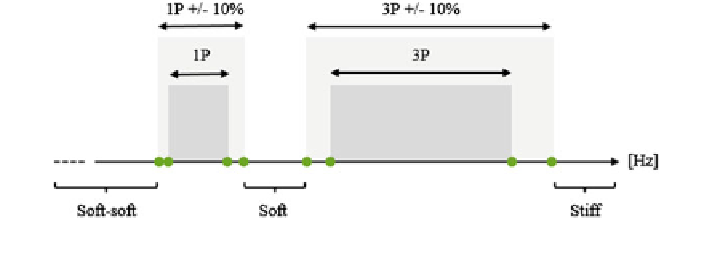
Fig. 12.1 Classification of wind turbine towers depending on the revolution frequencies of the
rotor blades
degree Of freedom (SDOF) system. Because of low damping values enormous
tower deflections can occur. During design process, in order to prevent these
resonant vibrations, the stiffness and therefore the fundamental frequency of the
tower are chosen depending on the rotor blade revolution frequencies. Hereby, the
rotational frequency of the rotor is called one-per-revolution frequency (1P).
Depending on the number of blades, the blade passing frequency is called two-per-
revolution (2P) or three-per-revolution frequency (3P). As shown in Fig.
12.1
,
according to the relationship between tower fundamental frequency and the rev-
olution frequencies of the rotor blades, wind turbine towers are classified as stiff,
soft, and soft-soft. The 1P and 3P regions shown in Fig.
12.1
are defined by the
cut-in and rated rotor speeds. Therefore, for instance, a soft tower can still
response resonantly during start-up phase below cut-in wind speeds. Depending on
the duration, this fatigue loading influences the lifetime of a wind turbine.
Turbulence wind loading depends on the average wind speed and turbulence
intensity. For the load calculations, several wind models are described in certifi-
cation documents for the wind turbines. Hereby, also the site-specific conditions
and interactions with other wind turbines can be taken into account.
The amplitudes of the turbulence-induced tower vibrations depend mainly on
the damping property of the plants, which consists of aerodynamic and structural
damping. The damping ratio of a wind turbine can be calculated by the logarithmic
damping decrement using the values in Table
12.1
[
13
]. According to this method,
a steel turbine tower has approximately a damping ratio of 1.4 %.
As mentioned before, the load change in the entire tower structure of a wind
turbine designed for 20 years corresponds to approximately 2
10
8
[
18
]. Half of the
Table 12.1 Logarithmic damping decrements and damping ratios of wind turbines [
13
]
Structural type
d
S
d
A
d = d
S
+ d
A
D = d/2p (%)
Steel tower
0.015
0.070
0.085
1.4
Concrete tower
0.040
0.060
0.100
1.6
d Logarithmic damping decrement
D Damping ratio