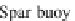Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
11.1 Introduction
With the steady increase in wind power worldwide, offshore wind farms are most
likely to be a sizable contributor of electricity production in some countries due to
the high quality of offshore wind resources and their proximity to the big shore
cities. To date, offshore wind turbines are limited to shallow water supported by
conventional fixed-bottom substructures [
1
]. Different types of substructures are
used according to water depth such as gravity bases for water depth to about 10 m,
fixed-bottom mono-piles for water depth to about 30 m, and tripods and lattice
frames used in water to about 50 m in depth [
1
]. For deeper water more than 60 m,
these support structures are no longer economically feasible and new types of
turbine support are needed. Floating support platforms are one of the potential
solutions. Numerous configurations of the floating support platforms are available
from the offshore oil and gas (O&G) industry. The technical feasibility of
developing offshore floating wind turbines platforms is out of question as the O&G
industry has already proven the long-term survivability of such support structures.
However, the main concern regarding this new trend to invade deep water is the
development of a cost-effective offshore floating wind turbine that can find its way
into the competitive energy market. This concern motivates the research for
optimized designs while making use of the gained knowledge from the offshore
O&G industry.
Floating substructures could be divided into three main concepts according to
the method used to achieve stability in pitch and roll. These three primary concepts
are the tension leg platform (TLP), spar buoy and barge (Fig.
11.1
). The TLP uses
mooring lines combined with excess buoyancy to provide restoring pitch and roll
moments, the spar buoy platform provides similar moments by its deep draft and
ballast, while the barge platform uses its shallow draft combined with the large
water-plane area moment to generate the needed restoring moments. Hybrid
Fig. 11.1
Floating platforms concepts