Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
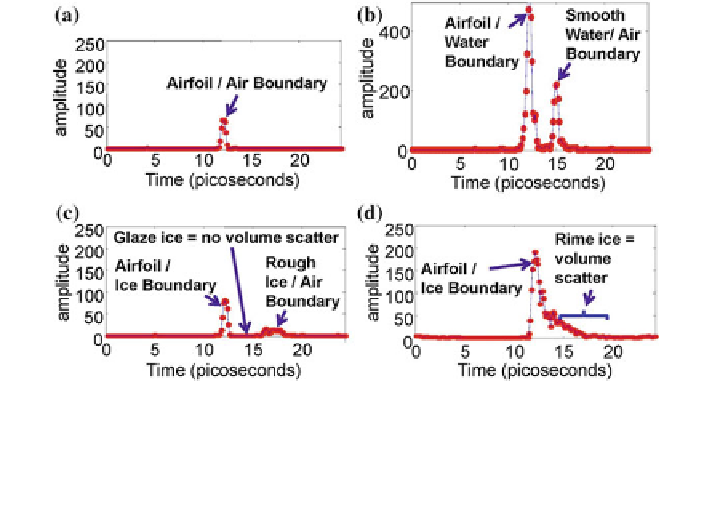
Fig. 8.9 OFDR measurements yield distinct signals for different conditions: a No water/ice on
the blade. b Liquid water on the blade. c Glaze ice on the blade. d Rime ice on the blade. Y-axis
is arbitrary scale proportional to the amplitude of the reflected optical electric field. X-axis is
round-trip optical time of flight from the fiber exit to the particular layer. 1 ps corresponds to a
round-trip travel time for the laser in 112.5 lm of water [
14
]. For ice thickness calculation, the
same index of refraction is assumed for ice and water
able to capture the volume scatter due to rime ice. The signal processing algorithm
looks at the number of captured peaks, peak magnitudes, magnitude of time integral
of the signals, and symmetrical/asymmetrical shape of the signals around their
peaks in order to detect the type of ice. For the case of water (Fig.
8.9
b), the
thickness of the water droplet is calculated by multiplying the speed of light by the
peak time difference between airfoil/water and water/air boundaries. For the case of
glaze ice (Fig.
8.9
c), the thickness of ice is calculated by multiplying the speed of
light by the peak time difference between airfoil/ice boundary and the first captured
peak of ice/air boundary. When there is rime ice (Fig.
8.9
d), the thickness is cal-
culated by multiplying the speed of light by the time difference between the airfoil/
ice boundary up to the time that volume scatter ends in the captured signal.
In summary, our demonstrated optical method is capable of direct detection of
ice existence, classification of ice type, and ice thickness measurement with 36
micrometer resolution.
8.6 Distributed Localized Heating
Due to varying amounts of heat loss in different regions of a rotating blade, an
energy efficient active de-icing method requires different amounts of thermal power
in different blade regions which motivates using distributed heating with adjustable
local heat flux to reduce power consumption for de-icing. The aerothermodynamic