Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
Bode Diagram
Wind Speed Unit Step Response
130
C1
C2
C4
0.4
120
0.3
0.2
110
0.1
0
100
-0.1
-0.2
90
-0.3
80
-0.4
10
0
0
20
40
Time (s)
Frequency (Hz)
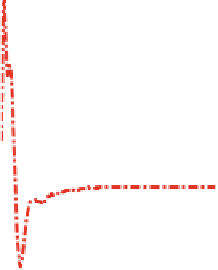
Fig. 5.20
Response of the rotor tilt moment for wind input
power production winds. On the other hand, two extreme load cases are ana-
lyzed: DLC1.6 and DLC1.9 cases. In these two analyses, the wind inputs are
different gusts and ramps respectively. Other extreme load cases are not taken
into account because results depend especially on the stop strategy, which has
not been very affected by the designed robust controllers.
According to the first step in the simulation analysis, one simulation is carefully
analyzed. The input of this simulation is a turbulent power production wind with a
mean speed of 19 m/s (Fig.
5.21
). The increase of the bandwidth of the output
sensitivity function in the pitch control loop achieved using the robust controllers,
mainly with the gain scheduled control in C3 (see Table
5.3
), improves the reg-
ulation of the generator speed near to the nominal value of 1,173 rpm for this wind
input (Fig.
5.22
).
Different signals are also analyzed in the frequency domain using the PSD
analysis. Figures
5.23
and
5.24
are focused on showing the influence of the
designed feedback robust control loops to load mitigation in wind turbines in
different variables. In this case, the C3 control strategy is not considered because
the improvement in the generator speed regulation does not considerably affect to
the load mitigation in power production wind cases. Figure
5.23
shows the pitch
contribution of the IPC in the pitch control angle set-points using C4 control
scheme. In this figure, the generator torque oscillations are reduced when the tower
side-to-side first mode damping is developed using the IPC instead of with the
generator torque control in C2 control strategy. The quality of the generated
electric power is better if the oscillations in the torque control are avoided using
C4 because the regulation of the generator speed is not affected by the pitch
contributions in each blade generated with the IPC.