Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
F
(
2
)
t
,1
F
(
2
)
t
,2
F
(
2
)
t
,3
F
(
2
)
t
,4
F
(
2
)
t
,5
F
(
2
)
t
,6
F
(
2
)
t
,7
F
(
2
)
t
,8
F
(
3
)
b
,1
F
(
3
)
b
,2
F
(
3
)
b
,3
F
(
3
)
b
,4
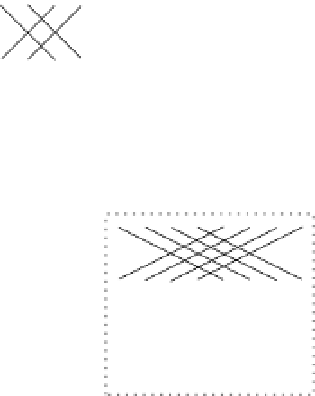
Figure 6.8
Decomposition of the 32-point FFT graph
F
(
5
)
into four copies of
F
(
3
)
and 8
copies of
F
(
2
)
. The edges between bottom and top sub-FFT graphs do not exist in the FFT
graph. They are used here to identify common vertices and highlight the communication needed
among sub-FFT graphs.
containing 2
d−e
copies of
F
(
e
)
and one stage containing 2
d−te
copies of
F
(
d−te
)
.The
result follows by setting
t
=
d/e
.
6.7.4 Convolution Theorem
The
convolution function
f
(
n
,
m
)
:
R
n
+
m
R
n
+
m−
1
over a commutative ring
maps an
n
-tuple
a
=(
a
0
,
a
1
,
...
,
a
n−
1
)
and an
m
-tuple
b
=(
b
0
,
b
1
,
...
,
b
m−
1
)
onto an
(
n
+
m
→
R
conv
−
1
)
-
tuple
c
, denoted
c
=
a
⊗
b
,where
c
j
is defined as follows:
c
j
=
r
+
s
=
j
a
r
∗
b
s
for 0
≤
j
≤
n
+
m
−
2
Here
and
. The direct computation of the
convolution function using the above formula takes
O
(
nm
)
steps. The convolution theorem
given below and the fast Fourier transform algorithm described above allow the convolution
function to be computed in
O
(
n
log
n
)
steps when
n
=
m
.
Associate with
a
and
b
the following polynomials in the variable
x
:
∗
are addition and multiplication over the ring
R
a
(
x
)=
a
0
+
a
1
x
+
a
2
x
2
+
+
a
n−
1
x
n−
1
···
b
(
x
)=
b
0
+
b
1
x
+
b
2
x
2
+
+
b
n−
1
x
n−
1
···
Then the coefficient of the term
x
j
in the product polynomial
c
(
x
)=
a
(
x
)
b
(
x
)
is clearly the
term
c
j
in the convolution
c
=
a
b
.
Convolution is used in signal processing and integer multiplication. In signal processing,
convolution describes the results of passing a signal through a linear filter. In binary integer
⊗

























































































































































































































































































































Search WWH ::

Custom Search