Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
X
∗
+
X
∗
WY
∗
VX
∗
f
(
n/
2
)
A
+
B
X
∗
WY
∗
VX
∗
f
(
n/
2
)
A
f
(
n/
2
)
A
+
B
×
B
X
∗
WY
∗
Y
∗
VX
∗
U
f
(
n/
2
)
A
f
(
n/
2
)
A
f
(
n/
2
)
A
×
B
×
B
×
B
X
∗
W
Y
∗
VX
∗
W
f
(
n/
2
)
A
f
(
n/
2
)
A
∗
f
(
n/
2
)
A
×
B
×
B
W
Y
V
X
∗
f
(
n/
2
)
A
∗
X
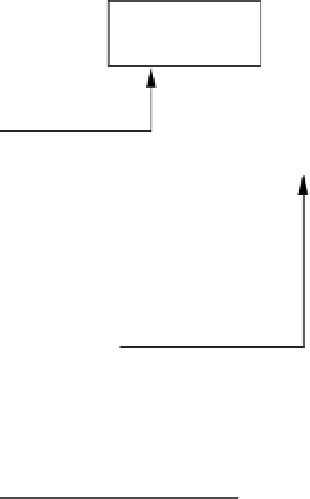
Figure 6.4
A circuit for the transitive closure of a Boolean matrix based on the construction of
equation (
6.4
).
c) for all
a
∈
S
,
a
+
0
=
0
+
a
=
a
;
d) for all
a
∈
S
,
a
·
1
=
1
·
a
=
a
;
e)
+
is commutative and
idempotent
;i.e.
a
+
a
=
a
;
f)
·
distributes over
+
;i.e.forall
a
,
b
,
c
∈
S
,
a
·
(
b
+
c
)=
a
·
b
+
a
·
c
and
(
b
+
c
)
·
a
=
b
·
a
+
c
·
a
.
The above definitions and results generalize to matrices over semirings. To show this, it suf-
fices to observe that the properties used to derive these results are just these properties. (See
Problem
6.12
.)
6.5 Matrix Inversion
The inverse of a non-singular
n
is another matrix
M
−
1
×
n
matrix
M
defined over a field
R
whose product with
M
is the
n
×
n
identity matrix
I
;thatis,
MM
−
1
=
M
−
1
M
=
I













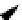





Search WWH ::

Custom Search