Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
a
b
Fig. 4.5
(
a
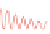
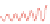
) Synaptic depression: decrease in the amplitude of the post-synaptic current (
b
) synap-
tic facilitation: increase in the amplitude of the post-synaptic current
4.6
Short- and Long-Term Plasticity
Short-term plasticity is distinguished from long-term plasticity and denotes a
change in the amplitude of the current appearing at the post-synaptic neuron, as
a consequence of spikes generated at the pre-synaptic neuron. An example is given
in the diagram of Fig.
4.5
and shows connection between cortical excitatory cells
(RS) and cortical fast synaptic units (FS) [
16
,
65
].
Next, it is explained how a pre-synaptic current affects the amplitude of the post-
synaptic current. One defines
M.t/ D q.t/f.t/
(4.20)
where q.t/2.0;1/ is the depression factor having as resting value q
0
and f.t/2.0;1/
is the facilitating factor having as resting value f
0
. The variation of f and q is
given by
f
d
dt
d
d
dt
D f
0
f;
D d
0
q
(4.21)