Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
3.3 Laccase (Lac): (EC 1.10.3.2)
Laccase belongs to a group of polyphenol oxidases in which the catalytic center is
found to be occupied by Cu atoms (Fernaud Hern
á
ndez et al.
2006
) This enzyme
was
rst discovered in the exudates of Japanese lacquer trees and then found in a
wide range of plants and fungi (Giardina et al.
2010
). Fungal laccases are found to
contain 4 Cu ions in three types of sites: type 1 (blue Cu) is characterized by a
strong absorption at
*
610 nm; type 2 is weakly absorbing and acts as a one-
electron acceptor; and type 3 contains a pair of Cu ions that absorb at 330 nm and
function as electron acceptors (Baldrian
2006
). Laccases have the ability to sur-
prisingly oxidize a wide range of organic and inorganic compounds including
diphenols, polyphenols,diamines, and aromatic amines by reducing molecular
oxygen to water (Kiiskinen et al.
2002
).
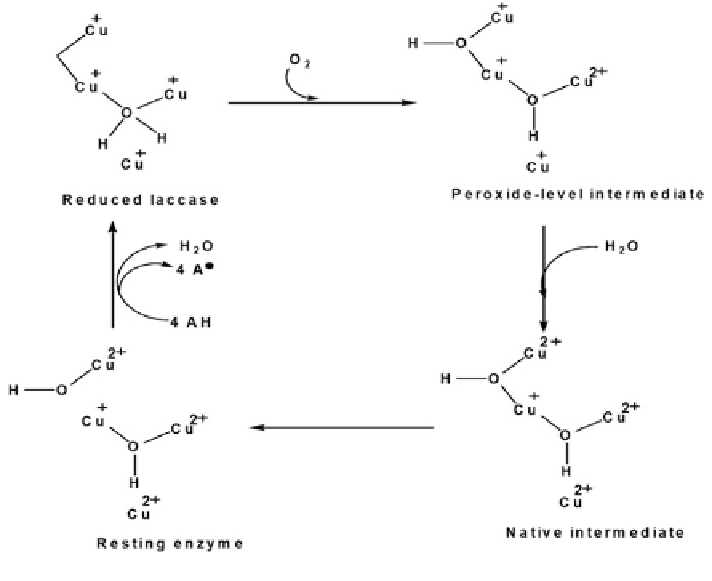
The function of fungal laccases is that four copper atoms are organized into 2
clusters; where type 1 copper is located near the active site and the 2 and type 3 are
located at the core of the enzyme forming a triangle and trinuclear cluster. The type
1 copper receives electrons extracted from the substrate and transfers it to type 3
copper, which subsequently relays the electrons to a type 2 copper where oxygen
gets reduced to water (Fig.
3
). For the reduction of oxygen, it is necessary that it
Fig. 3 Catalytic cycle of laccases (Wesenberg et al.
2003
)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search