Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
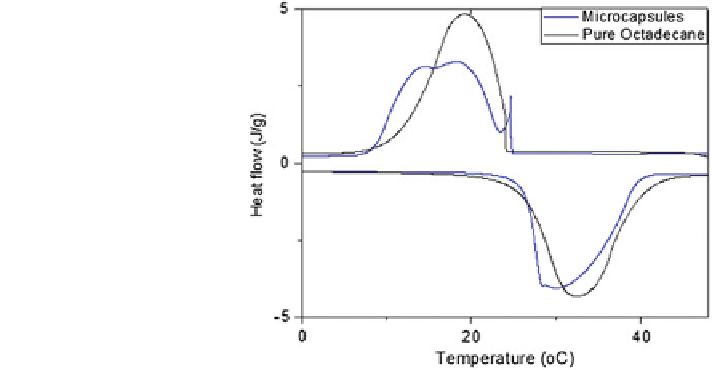
Fig. 3 DSC curves of bulk
and microencapsulated
paraffin n-C
18
H
38
is found to be 209 J/g by measuring the integral area of the single endothermic
peak on the bottom. The weight percentage of paraffin in the microcapsules is
about 88 %, by comparing the latent heat of the microcapsules and the bulk
paraffin.
Three peaks were observed on the cooling curve of the microcapsules, which is
different from the bulk curve with a single endothermic peak and a single exo-
thermic peak [
28
]. These DSC curves suggest that the microencapsulated n-C
18
H
38
first changes to a metastable rotator phase from melt rather than directly into the
solid triclinic phase, as for bulk n-C
18
H
38
. Later on, with temperature further
dropping, the metastable rotator phase converts to the stable triclinic phase. Based
on this analysis, the second exothermic peak with smaller subcooling is assigned to
the bulk crystallization from melt to a metastable rotator phase, while the third one
is the phase transition from the metastable rotator phase to the stable triclinic phase.
3.4 NPG-Silica Microcapsules (Solid-Solid PCM)
Certain molecular crystals, such as polyalcohols, undergo solid-state crystal
transformations that absorb sufficient latent heat; they can be used for practical
thermal energy storage and transfer application [
9
,
31
]. Those polyalcohols,
including neopentyl glycol (NPG), pentaerythritol (PE), etc., will transform from
heterogeneous crystals to homogeneously face-centered cubic (FCC) crystals with
high symmetry when the temperature rises across a certain point. A sufficient
latent heat is associated with such a solid-solid phase transition, due mainly to the
formation of hydrogen bonds among these molecules [
9
,
31
]. Compared to con-
ventional solid-liquid PCMs, the solid-solid PCMs do not involve the liquid
phase, so there is no concern about liquid leakage and thermal expansion during
Search WWH ::

Custom Search