Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
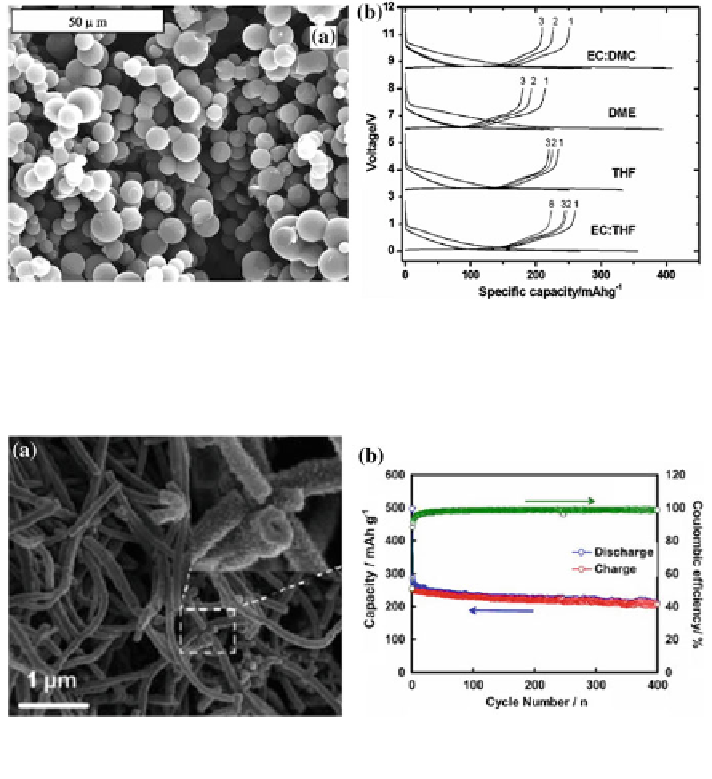
Fig. 21 SEM of carbon microspheres. b Voltage/capacity plots corresponding to the first
discharge/charge cycles of carbon aerogel microspheres in Na cells, 1 M NaClO
4
dissolved in
different solutions as electrolyte [
57
]
Fig. 22 a SEM images of the PANI-HNWs. b Cycle performance of the HCNW electrode at a
current density of 50 mA/g (0.2 C) [
58
]
EC-THF mixture electrolyte (Fig.
21
b). Cao et al. reported hollow carbon
nanowires (HCNWs) prepared by the pyrolyzation of a hollow polyaniline nano-
wire precursor (Fig.
22
a) [
58
]. The HCNW electrode delivered high reversible
capacity of 251 mAh g
-1
and excellent cycling stability (82.2 % of capacity
retention over 400 cycles) (Fig.
22
b). Such excellent electrochemical performance
was ascribed to the HCNWs that had a uniform hollow nanowire structure and an
appropriate interlayer distance, leading to short diffusion distance for Na insertion,
stable material structure, and feasible approach for Na-ion insertion into carbon
layers. Besides, Komaba et al. reported the effect of electrolytes on Na insertion
behavior in hard carbon [
59
]. It was found that in EC:DEC(1:1) solution con-
taining 1 mol L
-1
NaClO
4
, the hard carbon electrode exhibited a high capacity of
ca. 240 mAh g
-1
with a stable capacity retention over 100 cycles. This was related
Search WWH ::

Custom Search