Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
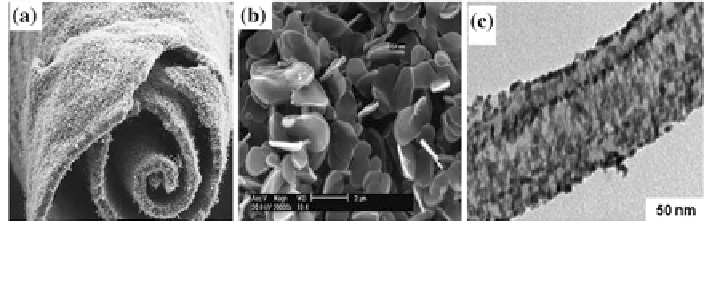
Fig. 2 a TEM image of carbon scrolls, b SEM image of coin like hollow carbon and c TEM
images of Pt deposited carbon nanofibers (adapted from Refs. [
37
,
40
] with permission from
American Chemical Society)
associated with fuel cells mainly in terms of durability and performance, carbon
nanotubes (CNTs) with its unique properties can actually do alleviate some critical
problems.
5.2 Carbon Nanotubes as Electrode Material for PEMFCs
Carbon nanotubes comes under the carbonaceous material with distinct charac-
teristics, like inertness under various chemical environments, highest Young's
modulus, electrical conductivity, high surface area, lightweight and easy inter-
facing capability with many inorganic and organic compounds [
43
-
47
]. CNTs can
be broadly classified into two types, single-walled and multiwalled CNTs with
reports available on even double-walled nanotubes [
48
-
52
]. CNTs are considered
as analogous to fullerenes due to the similarities in the electronic structure.
Moreover, many recent reports have clearly illustrated that the unique electronic
structure of CNTs helps in enhancing the catalytic activity of the supported metal
in addition to providing mechanical integrity [
53
-
56
]. For example, nitrogen- or
boron-doped CNTs can replace Pt as an electrocatalyst and there is a lot of
excitement on developing these types of new nanostructured electrocatalysts. In
this section we discuss current efforts on the use of CNTs in polymer electrolyte
fuel cells in both electrodes and electrolytes illustrating their multifunctional role
as catalyst layer, support and sometimes as a reinforcing component in polymer
composite membranes. The impact of functionalized CNTs on the performance
and durability of the MEAs in increasing the longevity and improved performance
will be discussed in such manner to unravel their potential in reducing the cost of
the stack per kW. Besides the discussion on materials and general procedures for
functionalizing CNTs for PEMFC, the use of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes
using surface-engineered CNTs in particular is also illustrated with their advan-
tages and limitations using both single-walled and multiwalled CNTs.
Effective utilization of Pt nanoparticle is a key parameter in decreasing the cost
of the fuel cell stacks as very low Pt loading (few hundred microgram/cm
2
)
Search WWH ::

Custom Search