Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
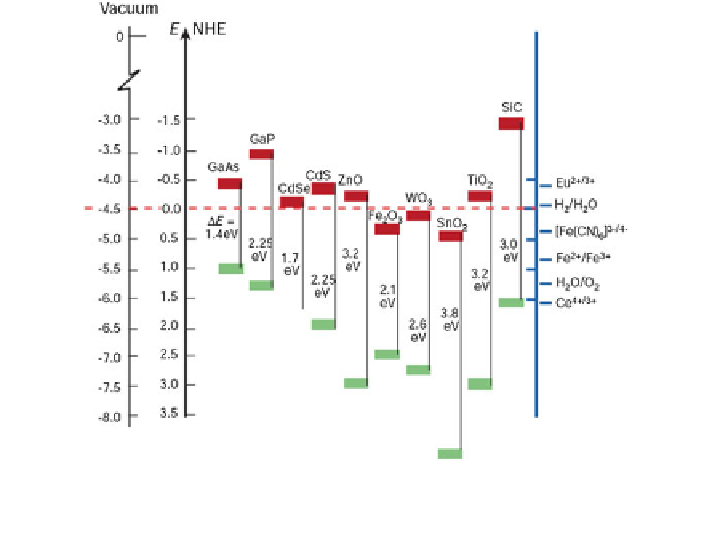
Fig. 2 Band edge positions of several semiconductors in contact with aqueous electrolyte at
pH 1 with energy scale versus vacuum level and the normal hydrogen electrode (NHE).
Reproduced with permission from [
23
]
WO
3
($40-60/Kg), and Fe
2
O
3
(less than $1/Kg) have been extensively studied
[
23
,
96
]. In this chapter, we will focus on the synthesis with low-cost techniques and
discuss their application in PEC water splitting.
2 Low-Cost Synthetic Methods
During the last two decades, a number of methods have been demonstrated for the
synthesis of metal oxide nanomaterials. Among these methods, hydrothermal and
solvothermal synthesis, sol-gel, electrochemical deposition, and anodization
method show great promise as low-cost and scalable approaches to prepare
nanomaterials for photoelectrodes, as these methods require simple equipment and
mild synthetic conditions. In this section, we are going to give a brief overview of
these low-cost synthetic methods.
2.1 Hydrothermal and Solvothermal Method
Hydrothermal synthesis is one of the most extensively used approaches to prepare
metal oxide nanomaterials such as TiO
2
[
97
,
101
], WO
3
[
33
,
85
,
99
], ZnO [
24
,
102
,
111
] and Fe
2
O
3
[
47
,
48
]. Hydrothermal synthesis is typically performed in a
Search WWH ::

Custom Search