Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
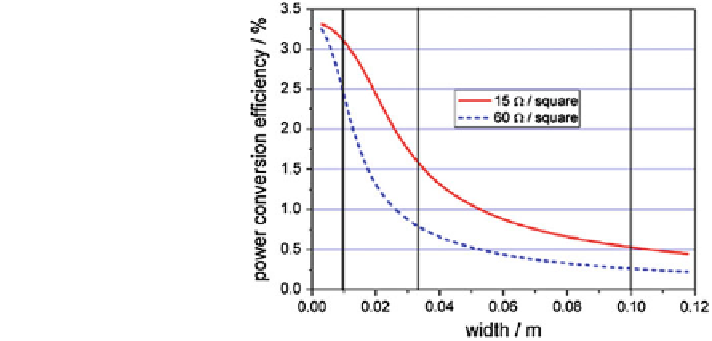
Fig. 31 Calculated power
conversion efficiency of a
P3HT:PCBM-based single
rectangular organic solar cell
as a function of the width of
the electrode. Two cases are
shown, an ITO sheet
resistance of 15 X/sq (solid
line) and 60 X/sq (dashed
line). Reproduced from [
24
]
with permission from
Elsevier 2007
investigated by Lungenschmied et al. [
24
]. They calculated theoretical power
conversion efficiencies of a P3HT:PCBM BHJ cells with two cases of ITO sheet
resistance, 15 and 60 X/sq. As shown in Fig.
31
, the rapid decrease of the power
conversion efficiency with increasing width of the rectangular solar cell can be
observed while the length of the device kept same, indicating that the performance
of stripe typed large area OPV devices are mainly affected by the width of the
stripes as a result of the series resistance of the transparent electrode.
Another effective way to reduce the R
S
of transparent electrode is the combi-
nation of metal mesh and PEDOT:PSS to serve as transparent electrode [
25
]. By
increasing the metal width and reducing the mesh period, the sheet resistance can
be made smaller than the conventional ITO electrode. A trade-off between the
optical transmittance and electrical conductivity still exists, though much smaller
than that of ITO [
25
]. This trade-off can be further compensated by embedding
high aspect-ratio metal mesh into conductive polymer, which eliminates the low
optical transmittance problem without sacrificing the conductivity. Kuang et al.
[
23
] fabricated a nanoscale metallic grating with optical transparency over 80 %
and low electrical resistance under 2.4 X/sq. To make the structure, a polyurethane
(PU) grating structure was prepared for oblique metal deposition and argon ion
milling process to get the metal layers on the PU sidewalls. The typical sheet
resistance of the patterned structures with gold and silver were 9.6 and 3.2 X/sq,
respectively, which are lower than the sheet resistance of ITO for typical appli-
cations of OPVs and OLEDs.
2.5.8 Fine Metal Mesh Design for Transparent Electrode
Previously, we demonstrated normal type OPVs by using fine transparent metal
mesh electrodes (TME) made by nanoimprinting [
25
] and transfer-printing [
26
]
techniques.
Recently,
we
fabricated
TME
by
conventional
photolithography
Search WWH ::

Custom Search