Environmental Engineering Reference
In-Depth Information
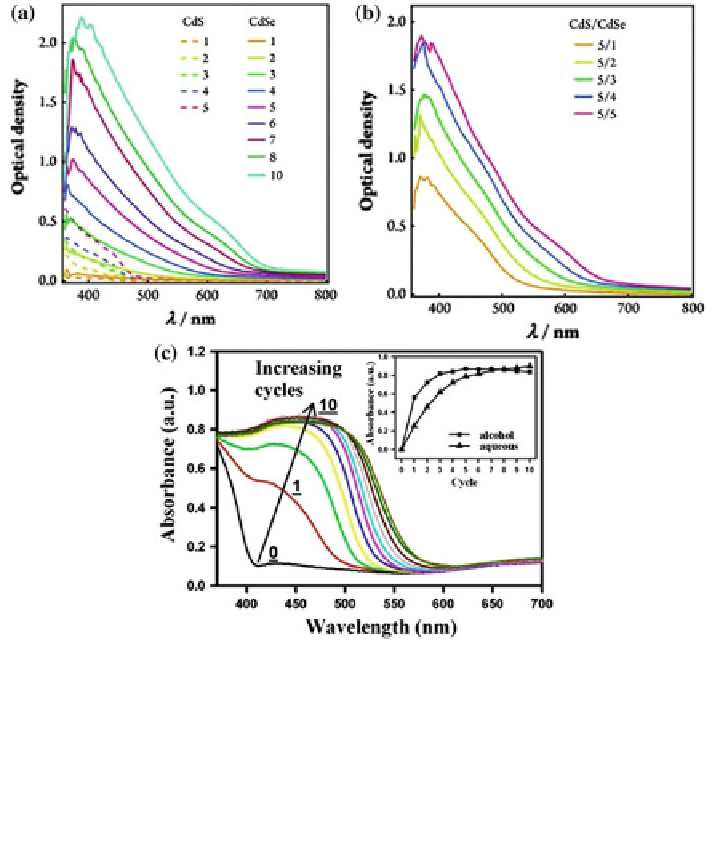
Fig. 4 UV-visible optical density (OD) spectra of as-prepared (a) nCdS and nCdSe, and
(b) 5CdS/nCdSe-coated 2.4 mm TiO
2
electrodes, where n is the number of SILAR deposition
cycles. The OD spectra represent the net light absorption by the sensitizers as the substrate
absorption (mesoporous TiO
2
) was subtracted from the absorption spectra of corresponding
nCdS, nCdSe and 5CdS/nCdSe-sensitized TiO
2
electrodes [Hossian et al. reprinted with
permission from RSC] [
77
](c) UV-vis absorption spectra of TiO
2
with different coating cycles of
CdS QDs in alcohol solutions. The inset shows the absorbance of excitonic peaks after various
cycles of the CBD process for alcohol and aqueous systems [Chang et al. [
45
] reprinted
permission from AIP publishers]
3.4 Electrodeposition
Electrodeposition (ED) is an emerging technique for synthesizing semiconductor
thin films and nanostructures, especially chalcogenides and oxides [
79
-
85
]. One of
the great advantages of ED method is that they are more suitable for solar cells
application [
86
,
87
] since it allows the possibility of easily altering both the
bandgap and lattice constant by composition modulation through the control of
growth parameters such as applied potential, pH, and temperature of the bath.
Thus, it is at least in principle possible to easily grow large areas of tandem cells
Search WWH ::

Custom Search