Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
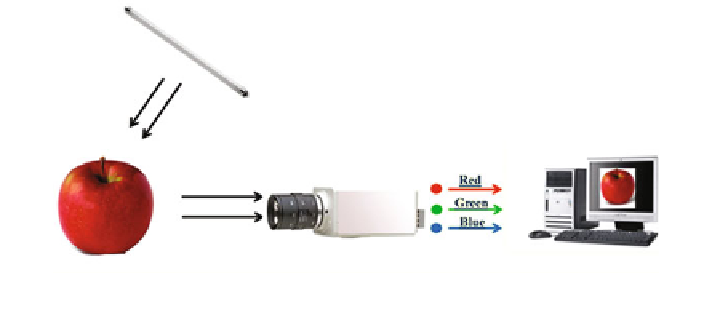
Fig. 4.2
A basic computer vision system schema
light (light source), the interaction of light with materials and the physiology of
human vision.
It is known that a light source comprises any process able to emit, re-emit, or
conduct energy in sufficient quantities to produce light, in other words, produces
electromagnetic radiation whose wavelengths are inside the visible region. There
are basically two types of light sources: natural light, such as the sun, and artificial
light, which can be based on different types of technologies, such as incandescent
lamps, fluorescent lamps, LEDs, among others. The distribution of the electro-
magnetic radiation emitted by these lamps depends on the emission material and
the conditions of its use.
The electromagnetic radiation originating from the light sources interacts with
various types of materials. Each material has its own characteristics due to their
molecular formation, thus presenting different properties when it interacts with
light. The result is the material color, which depends on its pigment constituents.
Therefore, a beam of radiation that is emitted can undergo reflection, trans-
mission, or absorption when it focuses on a particular material. It is noteworthy
that every material absorbs radiation in some part of the electromagnetic spectrum
and the quantity of energy absorbed relies on the selectivity of the absorbing
material (pigment) and the wavelength of the radiation.
Thus, one can consider two different types of color: the color originating from a
light source and the color pigment originating from a particular material, making
the task of specifying color impossible without including the knowledge of the
radiation source, since it provides the light that is reflected by the material that, in
turn, causes the color perception in the human eye, as shown by Fig.
4.3
.
The electromagnetic radiation emitted from light sources or from objects due to
reflection or transmission is perceived by the human vision system with the
photosensitive cells present in the retina, as seen above in Fig.
4.3
. The physiology
of the human eye states that the retina is composed of two types of receptor cells
that, due to their shapes, are called rods and cones. The cones are found primarily
in the center of the retina and are responsible for vision with higher brightness,
known as photopic vision. They are also responsible for color vision, being
Search WWH ::

Custom Search