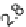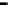Information Technology Reference
In-Depth Information
Percentage Graph Model Test2
100%
90%
80%
70%
60%
3
2
1
50%
40%
30%
20%
10%
0%
Fig. 14.3
100 % stacked area chart of evaluative distance [
X
-axis] against likelihood of choice
[
Y
-axis]
The hypothesis here is that an actor tends to choose others who have a similar view
of the music. For the results analysis, the relative z-score distance measure is used to
calculate the similarity between each pair of actors. The principle used is that those
closest in four-dimensional music space tend to be chosen as the ally. Closeness is
derived from the normal application of Pythagoras' theorem applied to a relative 4
dimensional z-score music space. Figure
14.3
shows a cumulative frequency graph
giving the proportion of position choice against distance. Those closest (z-score
distance of less than 0.8) are 100 % likely to be chosen but at distances approaching
a relative z-score of 4 all ally positions are accounted for. Thus at this high inclusive
distance all people that can be selected are included.
In Fig.
14.3
the blue area occupying the bottom left quadrant of the graph shows
the likelihood of a first ally being selected as the inclusive distance is extended.
When the evaluative distance is at its closest, a z-score of 0.4, then the likelihood
of first choice is a certainty. As the distance increases the likelihood begins to even
out between the first, second (red) and third (yellow) choices because more people
are being included. The position of no correlation between closeness and ally choice
would give the result that all ally choice positions would be equally likely for all
relative z-scores.
14.5
Model Running Results Analysis
Seven experimental runs of our model were done using the start conditions of the
seven actual experiments with people.
A model was developed to simulate how one participant can acquire another's
internal view of music through conversation and inference using simplified questions
without directly asking about their scale. We set the model up by using for each
subject the actual initial scores expressed during our experiments. We refer here
to the model of a subject as an actor since the software is playing the part of an